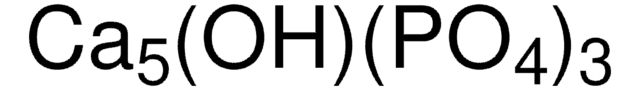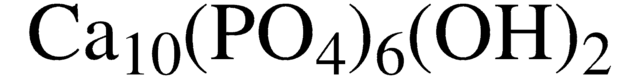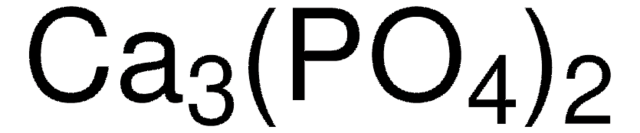677418
Fosfato de cálcio
nanopowder, <200 nm particle size (BET), ≥97%, synthetic
Sinônimo(s):
Fosfato de cálcio tribásico, HAp, Hidroxifosfato de cálcio, Hidroxilapatita
About This Item
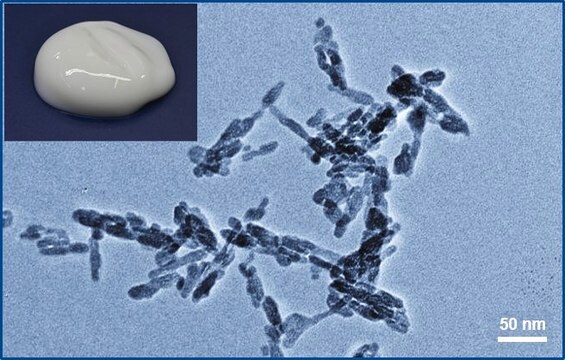
solid
Produtos recomendados
Nível de qualidade
Ensaio
≥97%
Formulário
nanopowder
solid
área da superfície
>9.4 m2/g
tamanho de partícula
<200 nm (BET)
pf
1100 °C (lit.)
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
[Ca++].[Ca++].[Ca++].[Ca++].O[Ca+].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O
InChI
1S/5Ca.3H3O4P.H2O/c;;;;;3*1-5(2,3)4;/h;;;;;3*(H3,1,2,3,4);1H2/q5*+2;;;;/p-10
chave InChI
XYJRXVWERLGGKC-UHFFFAOYSA-D
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Descrição geral
Aplicação
Poly (sodium 4-styrene sulfonate)-modified hydroxyapatite nanoparticles can be used as a drug carrier for vancomycin. Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles control the release of antibiotics after the implantation of a scaffold in the body.
Porous hydroxyapatite microspheres exhibit a high adsorptive capacity for heavy metals and can be used for the treatment of heavy metal contaminated water.
Características e benefícios
- Bioactive and biocompatible
- Good mechanical strength
- Porous structure
- Osteoconductive and osteointegrative properties
Informações legais
Código de classe de armazenamento
13 - Non Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 1
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Artigos
Dendrimers are just one class of nano-sized materials that are explored to develop new life-saving technologies. Single-wall carbon nanotubes are used to make miniaturized sensors for DNA, pathogens, and chemicals – for example glucose sensors. Multi-wall nanotubes, nanoclays, and ceramic nanoparticles are incorporated in ultra-strong polymer nanocomposites that will be used in orthopedic, for example joint-replacement, applications.
Innovation in dental restorative materials is driven by the need for biocompatible and natural-appearing restoration alternatives. Conventional dental materials like amalgam and composite resins have inherent disadvantages.
A key challenge for nanomaterial safety assessment is the ability to handle the large number of newly engineered nanomaterials (ENMs), including developing cost-effective methods that can be used for hazard screening.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica