900889
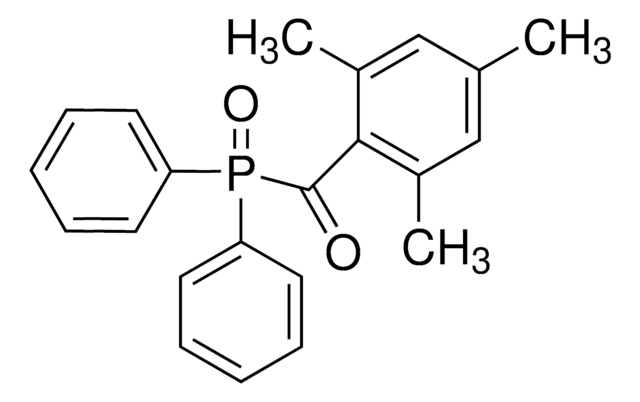
Lithium phenyl-2,4,6-trimethylbenzoylphosphinate
≥95%
Sinônimo(s):
LAP
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Nível de qualidade
Ensaio
≥95%
Formulário
crystalline powder
cor
white to off-white
temperatura de armazenamento
2-8°C
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
CC1=C(C(P(C2=CC=CC=C2)(O[Li])=O)=O)C(C)=CC(C)=C1
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Aplicação
Características e benefícios
- Superior water solubility
- Biocompatible
- Sensitiveto visible light
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Artigos
The introduction of LAP and water-dispersible photoinitiator nanoparticles of TPO, enables the development of novel formulations for 3D bioprinting, tissue engineering applications, and device manufacturing.
Conteúdo relacionado
Tissue engineering fabricates tissues cultures from scaffolds, living cells, and biologically active molecules by simulating the microenvironment of the body to repair or replace damaged tissue.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica