774022
Yttrium(III) oxide
sputtering target, diam. × thickness 2.00 in. × 0.25 in., 99.99% trace metals basis
Sinônimo(s):
Yttria
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Ensaio
99.99% trace metals basis
Formulário
powder
adequação da reação
core: yttrium
diâmetro × espessura
2.00 in. × 0.25 in.
pf
2410 °C (lit.)
densidade
5.01 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
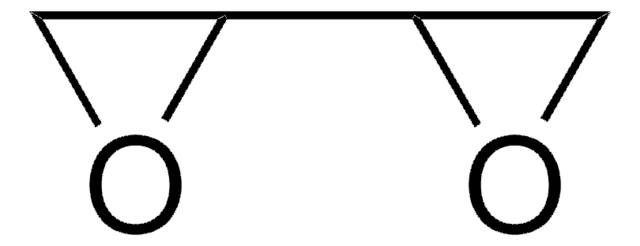
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
O=[Y]O[Y]=O
InChI
1S/3O.2Y
chave InChI
SIWVEOZUMHYXCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Aplicação
Yttrium oxide sputtering target can be used for physical vapor deposition of thin films of yttria stabilized zirconia layers for IT-SOFC. Yttrium containing films are used as thermal barrier and protective coatings in thermoelectric devices, rare earth doped yttrium oxide films are studied for phosphor applications.
Código de classe de armazenamento
13 - Non Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 1
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Certificados de análise (COA)
Não está vendo a versão correta?
Se precisar de uma versão específica, você pode procurar um certificado específico pelo número do lote ou da remessa.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Artigos
Spin-based electronic (spintronic) devices offer significant improvement to the limits of conventional charge-based memory and logic devices which suffer from high power usage, leakage current, performance saturation, and device complexity.
The properties of many devices are limited by the intrinsic properties of the materials that compose them.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica




![Poly[4,5-difluoro-2,2-bis(trifluoromethyl)-1,3-dioxole-co-tetrafluoroethylene] dioxole 87 mol %](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/951/320/21327fcd-4960-402d-8ae1-bf2e379cb2e2/640/21327fcd-4960-402d-8ae1-bf2e379cb2e2.png)