755745
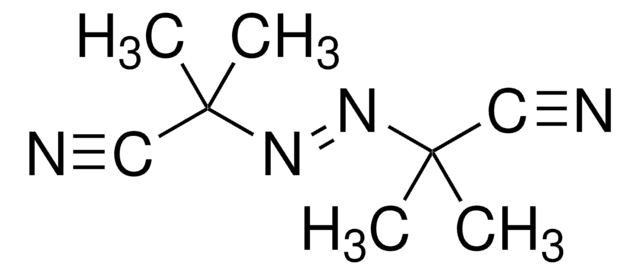
2,2′-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile)
recrystallized from methanol, 99%
Sinônimo(s):
α,α′-Azoisobutyronitrile, AIBN, Azobisisobutyronitrile, Free radical initiator
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Nível de qualidade
Ensaio
99%
Formulário
crystals
pf
102-104 °C (dec.) (lit.)
103-107 °C
temperatura de armazenamento
−20°C
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
CC(C)(\N=N\C(C)(C)C#N)C#N
InChI
1S/C8H12N4/c1-7(2,5-9)11-12-8(3,4)6-10/h1-4H3/b12-11+
chave InChI
OZAIFHULBGXAKX-VAWYXSNFSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Descrição geral
Aplicação
- Porous Acid-Base Hybrid Polymers for Enhanced NH3 Uptake: This study discusses the use of 2,2′-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) in the synthesis of acid-base hybrid polymers, highlighting its role in enhancing ammonia uptake through cooperative hydrogen bonds (X Luo, Y Liu, et al., 2023).
- Extraction of Fluoroquinolones from Milk: The development of molecularly imprinted polymers using 2,2′-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) as an initiator for the extraction of antibiotics from milk showcases its application in food safety and pharmaceutical analysis (E Megias-Pérez, et al., 2023).
- Thermo-responsive Copolymer Visible Light Catalyst: Highlighting the use of 2,2′-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) in the synthesis of thermo-responsive copolymers, this study explores its applications in catalysis and material science, particularly in photoreactive polymers (S Wu, et al., 2024).
Palavra indicadora
Danger
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 3 - Self-react. C
Perigos de suplementos
Código de classe de armazenamento
4.1A - Other explosive hazardous materials
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 2
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
122.0 °F
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
50 °C
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica