700339
Titanium(IV) oxide, mixture of rutile and anatase
nanoparticles, <100 nm particle size, dispersion, 48-52 wt. % in xylene, 99.9% trace metals basis
Sinônimo(s):
Titanium dioxide
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Ensaio
99.9% trace metals basis
Formulário
dispersion
nanoparticles
concentração
48-52 wt. % in xylene
tamanho de partícula
<100 nm
~30 nm (primary particle size of starting nanopowder)
p.e.
>135 °C
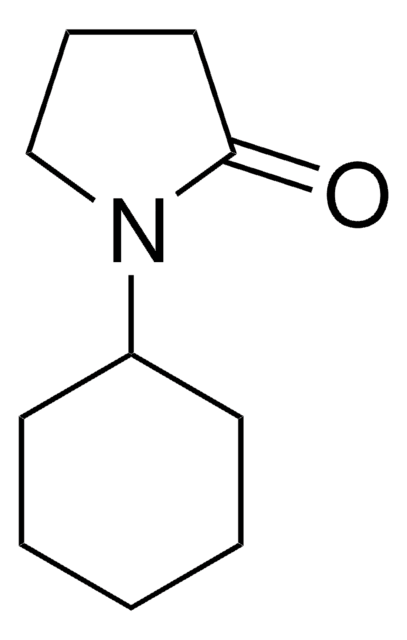
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
O=[Ti]=O
InChI
1S/2O.Ti
chave InChI
GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Descrição geral
Palavra indicadora
Danger
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Aquatic Chronic 3 - Asp. Tox. 1 - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 3 - Skin Corr. 1B - STOT RE 2 Inhalation - STOT SE 3
Órgãos-alvo
Central nervous system,Liver,Kidney, Respiratory system
Código de classe de armazenamento
3 - Flammable liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
80.6 °F
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
27 °C
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Artigos
Dye-sensitized solar cells directly convert sunlight to electricity
Over the last decade, dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) have attracted much attention because these unconventional solar cells exhibit high performance and have the potential for low-cost production.
One of the more traditional photovoltaic devices, single crystalline silicon solar cells were invented more than 50 years ago, currently make up 94% of the market. Single crystalline silicon solar cells operate on the principle of p-n junctions formed by joining p-type and n-type semiconductors.
Few Monolayer Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) on Surfaces and Interfaces for Energy Applications
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica