517933
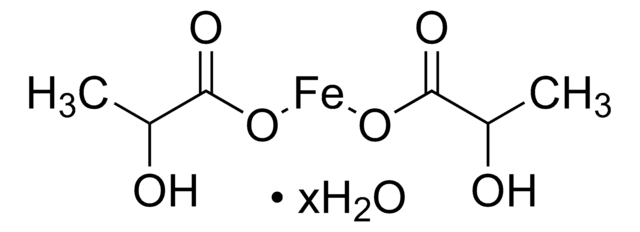
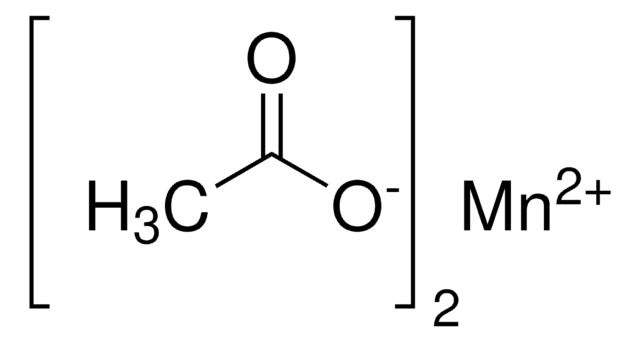
Iron(II) acetate
≥99.99% trace metals basis
Sinônimo(s):
Ferrous acetate, Iron acetate [Fe(OAc)2 ], Iron diacetate
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Ensaio
≥99.99% trace metals basis
Formulário
solid
adequação da reação
core: iron
pf
190-200 °C (dec.) (lit.)
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
CC(=O)O[Fe]OC(C)=O
InChI
1S/2C2H4O2.Fe/c2*1-2(3)4;/h2*1H3,(H,3,4);/q;;+2/p-2
chave InChI
LNOZJRCUHSPCDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Descrição geral
Aplicação
- A precursor for synthesizing iron oxide and iron-based nanostructures which are employed as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries and supercapacitors.
- A precursor in the synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles. These particles are incorporated into carbon nanofibers for use in supercapacitor applications.
- A precursor to synthesize hematite nanoparticles for applications in solar cells. These nanoparticles exhibit shape-dependent optical properties and can be used for imaging, photocatalysis, and solar cells. The product was used to synthesize iron oxide nanoparticles which was further used to form iron oxide-poly(ethylene glycol) core-shell nanoparticles (NPs). The core-shell NPs were studied for self-assembly at liquid–liquid interfaces (SALI) forming monolayers.
Embalagem
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Artigos
Professor Randal Lee (University of Houston, USA) discusses design considerations for iron oxide magnetic nanospheres and nanocubes used for biosensing, including synthetic procedures, size, and shape. The effects of these variables are discussed for various volumetric-based and surface-based detection schemes.
Magnetism and magnetic materials have been of scientific interest for over 1,000 years. More recently, fundamental investigations have focused on exploring the various types of magnetic materials and understanding the magnetic effects created by electric currents.
The properties of many devices are limited by the intrinsic properties of the materials that compose them.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica