50384
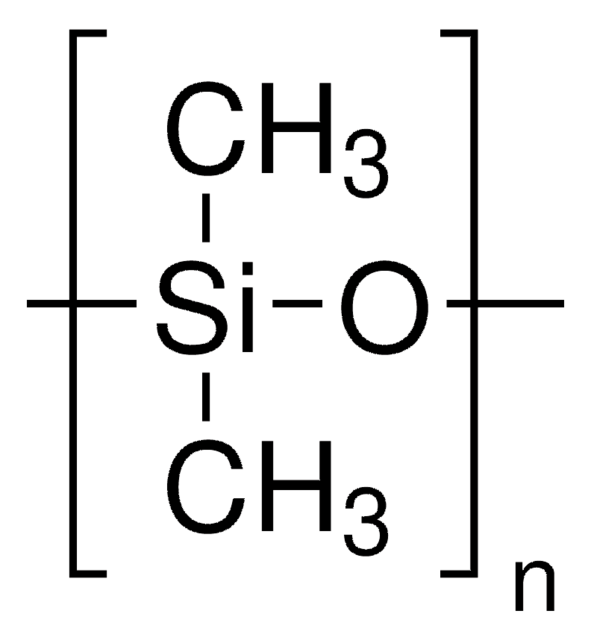
Silicone oil AP 150
viscosity ~150 mPa.s, neat(25 °C)
Sinônimo(s):
Silicone fluid
Faça loginpara ver os preços organizacionais e de contrato
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Descrição geral
Silicone oil AP 150 is a conventional electrorheologic (ER) fluid. It was employed as an insulating medium during the poling of hard ferroelectric ceramics. Silicon oil is composed of a mixture of hydrophobic polymeric and monomeric compounds, containing silicon-oxygen bonds. Its physical and chemical characteristics have been reported. The utility of silicon oil as a vitreous substitute has been studied.
Aplicação
Silicone oil AP 150 was used to prevent the water evaporation during rheological characterization of injectable polysaccharide system based on calcium alginate hydrogel and two dextran methacrylate derivatives. It may be used for the determination of chloroplast volume by the silicone oil filtering centrifugation technique.
Código de classe de armazenamento
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
437.0 °F - closed cup
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
225.00 °C - closed cup
Equipamento de proteção individual
Eyeshields, Gloves
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Silicone Oil: Different Physical Proprieties and Clinical Applications.
Barca F, et al.
BioMed Research International, 2014 (2014)
Poling of hard ferroelectric PZT ceramics.
Kamel TMand de With G.
J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 28(9), 1827-1838 (2008)
L Pescosolido et al.
European biophysics journal : EBJ, 39(6), 903-909 (2009-03-28)
A novel injectable polysaccharide system based on calcium Alginate (Ca-Alg) hydrogel and two Dextran methacrylate derivatives (DexMA) was recently developed. The resulting Interpenetrating Polymer Network showed a synergistic mechanical behavior that can be exploited to target the hydrogel properties towards
F Aliotta et al.
Physical review. E, Statistical, nonlinear, and soft matter physics, 87(6), 062304-062304 (2013-07-16)
The influence of interactions between particle surface and host fluids in electrorheological suspensions is explored. It is observed that dispersions of nanosized particles of titania in octanoid acid exhibit an anomalously large electrorheologic effect when compared with a similar dispersion
S P Robinson
Plant physiology, 79(4), 996-1002 (1985-12-01)
Spinach leaf chloroplasts isolated in isotonic media (330 millimolar sorbitol, -1.0 megapascals osmotic potential) had optimum rates of photosynthesis when assayed at -1.0 megapascals. When chloroplasts were isolated in hypertonic media (720 millimolar sorbitol, -2.0 megapascals osmotic potential) the optimum
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica