10836
Silicone oil AR 20
viscosity ~20 mPa.s, neat(25 °C)
Sinônimo(s):
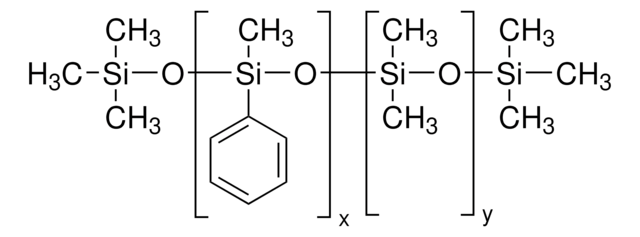
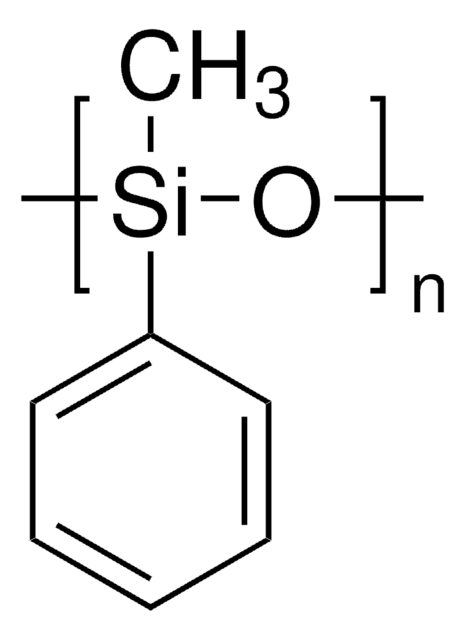
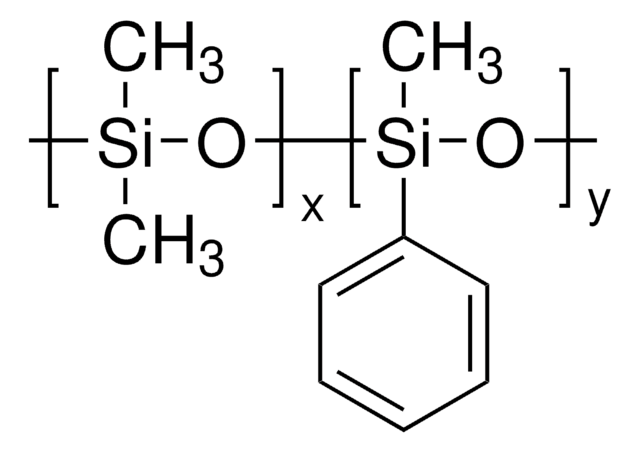
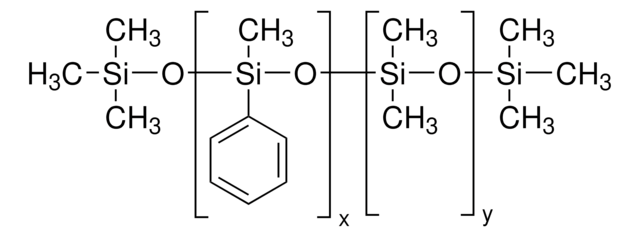
Polyphenyl-methylsiloxane
Faça loginpara ver os preços organizacionais e de contrato
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
índice de refração
n20/D 1.441-1.445
Nível de qualidade
viscosidade
~20 mPa.s, neat(25 °C)
densidade
1.000-1.020 g/mL at 20 °C
Categorias relacionadas
Descrição geral
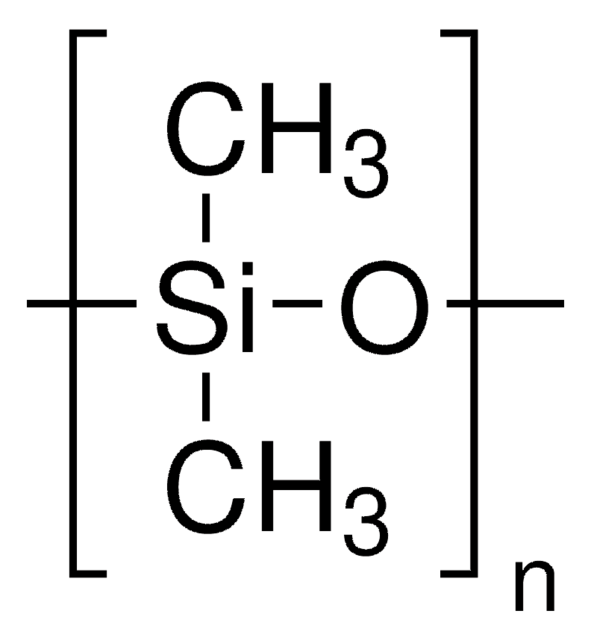
Silicone oil AR 20 is a polydimethylsiloxane with phenyl groups that is commonly used as a heat transfer or pressure transfer fluid.
Aplicação
Silicone oil AR 20 has been used:
- As a Segmenting fluid in polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
- In hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction (LPME) procedure for extraction of hydrophobic drugs from human breast milk.
- As a fluid to demonstrate pores in droplet interface bilayers (DIBs).
Características e benefícios
Especially good thermostability (-50°C to +230°C)
Código de classe de armazenamento
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
338.0 °F - Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
170 °C - Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
Eyeshields, Gloves
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Liquid-phase microextraction of drugs from human breast milk
Bj?rhovde, A, et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 491(2), 155-161 (2003)
Formation of droplet interface bilayers in a Teflon tube
Walsh E, et al.
Scientific reports, 6(2), 34355-34355 (2016)
E J Walsh et al.
Biomedical microdevices, 7(4), 269-272 (2006-01-13)
This paper evaluates the compatibility of segmenting fluids for two phase flow applications in biomedical microdevices. The evaluated fluids are chosen due to the variations in fluid properties and cost, while also reflecting their use in the recent literature. These
Helena L E Coker et al.
Biophysical journal, 116(6), 1085-1094 (2019-03-09)
Diffusion in cell membranes is not just simple two-dimensional Brownian motion but typically depends on the timescale of the observation. The physical origins of this anomalous subdiffusion are unresolved, and model systems capable of quantitative and reproducible control of membrane
Gema Flores et al.
Journal of chromatography. A, 1153(1-2), 29-35 (2007-02-20)
A method based on the use of absorbents as packing materials in the interface of the direct coupling between reversed phase liquid chromatography and gas chromatography (RPLC-GC) is proposed. To that end, a comparative study on different adsorbents and absorbents
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica