448869
Quitosana
low molecular weight
Sinônimo(s):
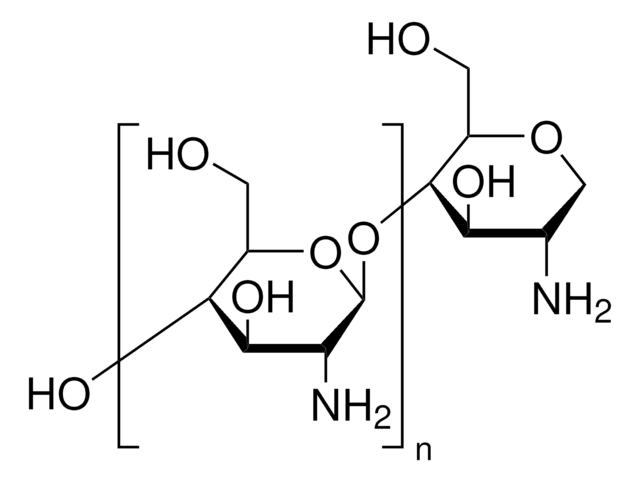
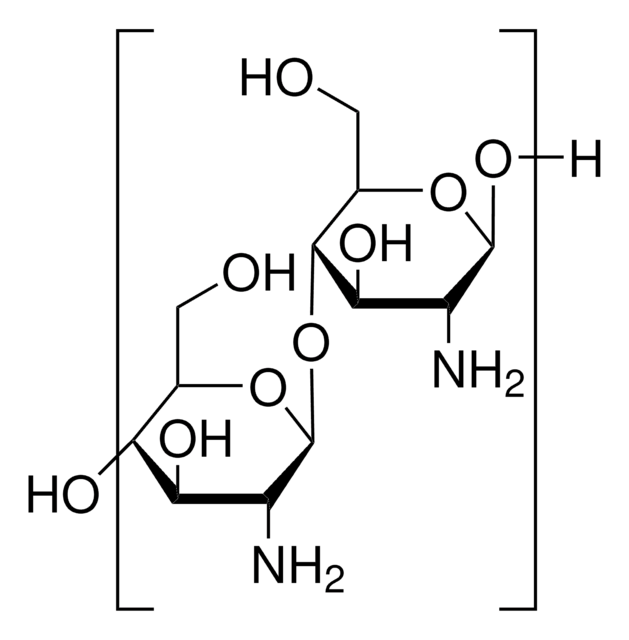
Poli(D-glicosamina), Quitina desacetilada
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Nível de qualidade
Formulário
powder
peso molecular
50,000-190,000 Da (based on viscosity)
viscosidade
20-300 cP, 1 wt. % in 1% acetic acid(25 °C, Brookfield)(lit.)
solubilidade
dilute aqueous acid: soluble
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
N([C@H]1[C@@H](O[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]1O)O[C@@H]4O[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]4N)O)O[C@@H]5O[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]5N)O)O[C@@H]6O[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]6N)O)O[C@@H]7O[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]7N)O)O[C@@H]8O[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]8N)O)O[C@@H]9O[C@@H]([C@H](
InChI
1S/C56H103N9O39/c1-87-56(86)65-28-38(84)46(19(10-74)96-55(28)104-45-18(9-73)95-49(27(64)37(45)83)97-39-12(3-67)88-47(85)20(57)31(39)77)103-54-26(63)36(82)44(17(8-72)94-54)102-53-25(62)35(81)43(16(7-71)93-53)101-52-24(61)34(80)42(15(6-70)92-52)100-51-23(60)33(79)41(14(5-69)91-51)99-50-22(59)32(78)40(13(4-68)90-50)98-48-21(58)30(76)29(75)11(2-66)89-48/h11-55,66-85H,2-10,57-64H2,1H3,(H,65,86)/t11-,12-,13-,14-,15-,16-,17-,18-,19-,20-,21-,22-,23-,24-,25-,26-,27-,28-,29-,30-,31-,32-,33-,34-,35-,36-,37-,38-,39-,40-,41-,42-,43-,44-,45-,46-,47-,48+,49+,50+,51+,52+,53+,54+,55+/m1/s1
chave InChI
FLASNYPZGWUPSU-SICDJOISSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Categorias relacionadas
Aplicação
Características e benefícios
forma física
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
nwg
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Certificados de análise (COA)
Não está vendo a versão correta?
Se precisar de uma versão específica, você pode procurar um certificado específico pelo número do lote ou da remessa.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Artigos
The development of new medical devices and pharmaceuticals plays an integral role in the medical industry. Both natural and synthetic polymers possess benefits that make them valuable components in therapeutics.
Microparticles with controlled size and morphology are of significant interest in the fields of drug delivery and biopharmaceuticals. The objective of this study was to assess the effect of processing parameters on the ability to control the size and distribution of chitosan based microparticles, targeting diameter range of 1-10 µm. The effect of encapsulating bovine serum albumin (BSA), a model protein, as well as sodium tripolyphosphate (TPP), a cross-linker, was studied.
Chitosan-based Biomaterials
Chitosan is a naturally occurring polysaccharide ideally suited for use in medical supplies, devices, therapeutics, and diagnostics. The unique natural characteristics of chitosan include its cationic, biocompatible, biodegradable, non-toxic, non-immunogenic, and antimicrobial properties.
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 448869-50G | 4061835563128 |
| 448869-250G | 4061835571628 |
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica