442631
Coumarin 6
98%
Sinônimo(s):
3-(2-Benzothiazolyl)-7-(diethylamino)coumarin, 3-(2-Benzothiazolyl)-N,N-diethylumbelliferylamine
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Nível de qualidade
Ensaio
98%
Formulário
solid
pf
208-210 °C (lit.)
λmax
444 nm
fluorescência
λem 505 nm in ethanol (Lasing peak 534 nm, lasing range 515 - 558 nm (DMSO), pump source XeCl (308 nm))
Desempenho do dispositivo OLED
ITO/Alq3:Coumarin 6/Mg:Ag
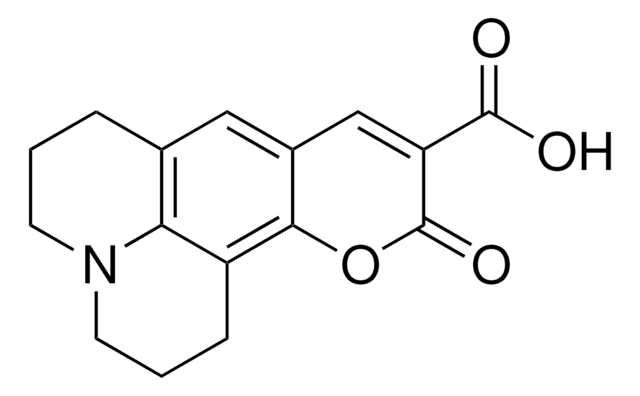
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
CCN(CC)c1ccc2C=C(C(=O)Oc2c1)c3nc4ccccc4s3
InChI
1S/C20H18N2O2S/c1-3-22(4-2)14-10-9-13-11-15(20(23)24-17(13)12-14)19-21-16-7-5-6-8-18(16)25-19/h5-12H,3-4H2,1-2H3
chave InChI
VBVAVBCYMYWNOU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Categorias relacionadas
Descrição geral
Aplicação
- in block copolymer (BCP)-based micelle based drug delivery studies in glioma cell lines
- in combination with flufenamic acid (FA) based nanoprodrug uptake in glioma cells
- in poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) based elvitegravir nanoprodrug uptake studies
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Artigos
One of the common difficulties with intravenous drug delivery is low solubility of the drug. The requirement for large quantities of saline to dissolve such materials limits their clinical use, and one solution for this problem that has recently generated interest is the formation of drug-loaded micelles.
Developed in the last several years, fluorescence quenching microscopy (FQM) has enabled rapid, inexpensive, and high-fidelity visualization of two-dimensional (2D) materials such as graphene-based sheets and MoS2.
Graphene has emerged as the new wonder material. Being only one atom thick and composed of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice structure, the interest in this material has exploded exponentially since 2004 when it was first isolated and identified using a very simple method.
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 442631-5G | 4061832282688 |
| 442631-1G | 4061832282671 |
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica