RPOLT7-RO
Roche
T7 RNA Polymerase
from Escherichia coli BL 21/pAR 1219
Synonyme(s) :
polymerase
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
Escherichia coli (BL 21/pAR 1219)
Niveau de qualité
Pureté
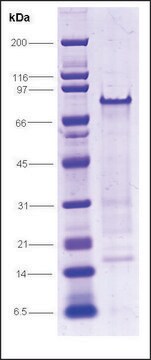
100% (SDS-PAGE)
Forme
solution
Activité spécifique
≥20 U/μL
Poids mol.
98 kDa (Single polypeptide chain)
Conditionnement
pkg of 1,000 U (10881767001)
pkg of 5,000 U (10881775001)
Fabricant/nom de marque
Roche
Technique(s)
Northern blotting: suitable
Southern blotting: suitable
hybridization: suitable
Couleur
colorless
pH
7.9 (39 °F)
Solubilité
water: miscible
Adéquation
suitable for molecular biology
Numéro d'accès NCBI
Numéro d'accès UniProt
Application(s)
life science and biopharma
Activité étrangère
Endonucleases 100 units, none detected
Nicking activity 100 units, none detected
RNase 100 units, none detected
Température de stockage
−20°C
Informations sur le gène
Escherichia coli ... T7p07(1261050)
Description générale
Synthesis of hybridization probes: T7 RNA polymerase allows highly efficient production of homogeneously labeled RNA. This labeled RNA may be used as hybridization probes in Southern, northern, and dot blots, as well as in situ hybridizations.
Suitable labels:Transcripts can be nonradioactively labeled with biotin-16-UTP or DIG-11-UTP. They may also be radioactively labeled to high specific activity with [α-32P]- or [α-35S]-labeled nucleotides.
Spécificité
T7 RNA polymerase is extremely promoter-specific and only transcribes bacteriophage T7 DNA or DNA cloned downstream of a T7 promoter. Although the T7 and T3 promoter sequences differ only by 3 bp, T7 RNA polymerase only transcribes DNA cloned downstream of its promoter.
Heat inactivation: Stop the reaction by adding 2 μl 0.2 M EDTA (pH 8.0) and/or heat to 65 °C.
Application
- T7 RNA Polymerase can transcribe RNA from cloned DNA templates that are downstream from a T7 promoter. The synthesis can be performed with labeled NTPs to generate highly labeled RNA. Synthesized RNA can be used in many applications, including: RNA or DNA blotting techniques
- In situ hybridization
- RNase protection studies: Transcripts synthesized by the enzyme are used as precursor RNA for studies on RNA splicing and processing.
- Synthesis of capped RNA in vitro with addition of m7GpppG or m7GpppA in excess over GTP or ATP during the transcription reaction. The generated antisense RNA can be introduced into cells to suppress the expression of the corresponding genes.
- Microarray target synthesis
Conditionnement
Définition de l'unité
Volume Activity: ≥20 U/μl
Notes préparatoires
Stockage et stabilité
Autres remarques
40 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0 (+20°C), 6 mM MgCl2, 10 mM dithiothreitol, 2 mM spermidine, pH approximately 8.0 (+20°C).
Absence of Endonucleases
1. 1 μg lambda DNA is incubated with T7 RNA polymerase for 4 hours at +37°C in 25 μl test buffer. The number of enzyme units which show no degradation of lambda DNA is >100 U.
2. 1 μg Eco RI/Hind III fragments of lambda DNA is incubated with T7 RNA polymerase for 4 hours at +37°C in 25 μl test buffer. The number of enzyme units which show no alteration of the banding pattern is >100 U.
Absence of Nicking Activity
1 μg pBR322 DNA is incubated with T7 RNA polymerase for 4 hours at +37°C in 25 μl test buffer. The number of enzyme units which show no relaxing of supercoiled structure is >100 U.
Absence of RNases
4 μg MS2 RNA are incubated with T7 RNA polymerase for 4 hours at +37°C in 50 μl test buffer. The number of enzyme units which show no degradation of MS2 RNA is >100 U.
Performance in Transcription Assay
T7 RNA polymerase is function tested in the SP6/T7 Transcription Kit (Cat. No. 10 999 644 001). The incorporation rate in the standard assay with 0.5 μg pSPT19 neo DNA linearized with Eco RI and 50 mCi [alpha-32P] CTP, [400 Ci/mmol (15 TBq/mmol)] gives >50% of the input radioactivity in 20 minutes.
Roche has 10x concentrated RNA Labeling Mixes that are specially designed for DIG- or biotin-labeling. These mixes work well with T7 RNA Polymerase.
Composants de kit seuls
- T7 RNA Polymerase, in buffer, pH 7.9 ≥20 U/μl
- Transcription Buffer 10x concentrated
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Eye Irrit. 2
Code de la classe de stockage
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Point d'éclair (°F)
does not flash
Point d'éclair (°C)
does not flash
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
T7 RNA Polymerase is a DNA-dependant RNA Polymerase that exhibits a very high specificity for the T7 promoter sequence.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique