Wichtige Dokumente
SBR00023
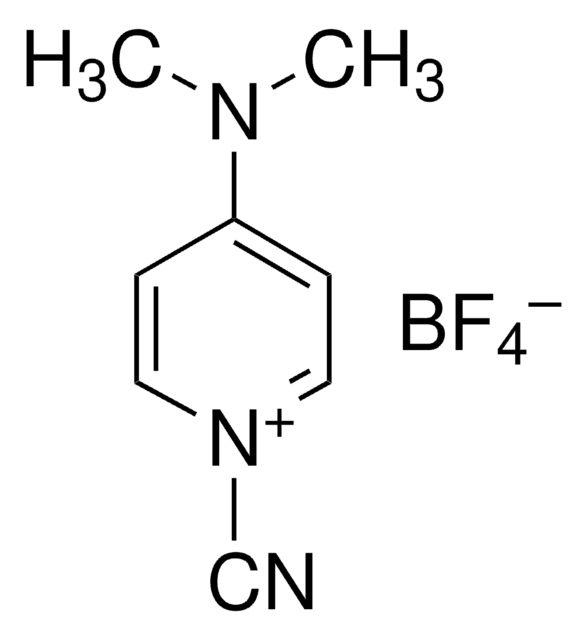
1-Cyano-4-dimethylaminopyridinium tetrafluoroborate Ready Made Solution
organic cyanylating reagent, 100 mg/mL in acetonitrile
Synonym(e):
4-(dimethylamino)pyridin-1-ium-1-carbonitrile tetrafluoroborate, CDAP
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Biologische Quelle
synthetic
Assay
≥97%
Form
liquid
Mol-Gew.
234.99
Konzentration
100 mg/mL in acetonitrile
Versandbedingung
dry ice
Lagertemp.
−20°C
SMILES String
[B-](F)(F)(F)F.[N+](=C1C=CN(C=C1)C#N)(C)C
InChI
1S/C8H10N3.BF4/c1-10(2)8-3-5-11(7-9)6-4-8;2-1(3,4)5/h3-6H,1-2H3;/q+1;-1
InChIKey
MBLVMDCQDCVKNE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
CDAP is considered to be a less toxic reagent as compared to cyanogen bromide (CNBr) (a known polysaccharides activator). In addition, CDAP is easier to use as it can be employed at a lower pH and has fewer side reactions. It is known that CDAP polysaccharide activation efficiency is optimal at pH 9-10. It was also reported that direct conjugation of protein to CDAP-activated polysaccharides can be performed under mildly alkaline conditions (pH 7-9). It has also been reported that proteins could also be conjugated to CDAP-activated polysaccharides at pH 5.
Leistungsmerkmale und Vorteile
- Readily available solution, that reduces the need for preparation time
- Versatile and adaptable for vaccine and biochemical research
Angaben zur Herstellung
Sonstige Hinweise
Signalwort
Danger
Gefahreneinstufungen
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Lagerklassenschlüssel
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
35.6 °F
Flammpunkt (°C)
2 °C
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Die passende Version wird nicht angezeigt?
Wenn Sie eine bestimmte Version benötigen, können Sie anhand der Lot- oder Chargennummer nach einem spezifischen Zertifikat suchen.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.