D8037
Driselase™ Basidiomycetes sp.
suitable for plant cell culture, BioReagent
Synonym(e):
Driselase™ aus Basidiomycetes ssp.
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(5)
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Produktlinie
BioReagent
Form
powder
Zusammensetzung
Protein, ≥10% biuret
Methode(n)
cell culture | plant: suitable
Anwendung(en)
agriculture
Lagertemp.
−20°C
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Anwendung
Driselase™ Basidiomycetes sp. wird wie folgt verwendet:
- bei der Sphäroplastenherstellung aus Coccomyxa-Zellen
- in einem Mutageneseprotokoll auf Basis von CRISPR/Cas9 für Brachypodium distachyon und sein verwandtes Allopolyploid Brachypodium hybridum
- für den Zellwandaufschluss zum Durchführen der Ganzpräparatimmunlokalisierung von Lotus japonicus Wurzelgewebe
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
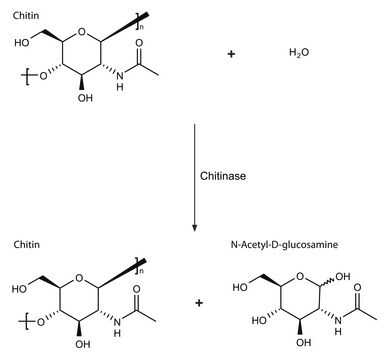
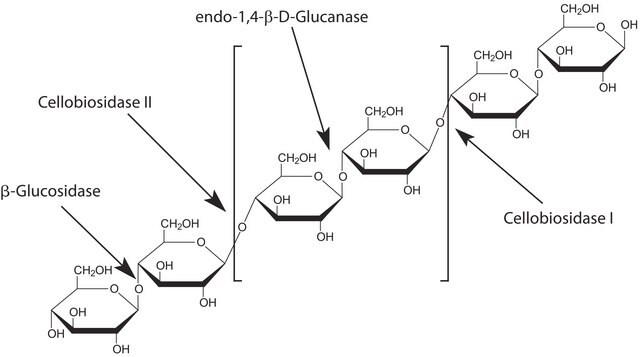
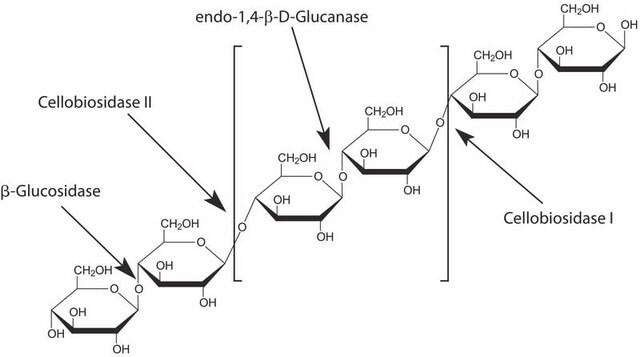
Driselase™ ist eine natürliche Mischung von Enzymaktivitäten (Kohlenhydrate aus Pilzen), die zum Aufschluss von Pflanzenzellwänden verwendet wird, um die Mazeration von Pflanzenmaterial, die Protoplastenbildung und Extraktionsprozesse zu erleichtern. Driselase setzt Zellwandkohlenhydrate frei. Diese Formulierung enthält die Enzymaktivitäten von Cellulose, Endo-1,3-β-glucanase und Xylanase.
Sonstige Hinweise
Rohes Pulver mit Laminarinase, Xylanase und Cellulase.
Rechtliche Hinweise
Driselase is a trademark of ASKA Animal Health Co. Ltd.
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
P-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Resp. Sens. 1
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
G J McDougall et al.
Carbohydrate research, 219, 123-132 (1991-10-14)
The retention times of 10 oligosaccharides, generated from the xyloglucans of Rosa and Tropaeolum by the action of Trichoderma cellulase, and of 17 related carbohydrates, in h.p.l.c. on an amino-substituted silica (Amino-Spheri-5) depended largely on the number of hydroxyl groups
M C Ralet et al.
Carbohydrate research, 263(2), 227-241 (1994-10-17)
Cell walls from sugar-beet pulp contain some feruloyl groups linked to the pectic neutral side-chains. Enzymic as well as chemical hydrolysis of the pulp yielded a series of feruloylated oligosaccharides, which have been purified by Sephadex LH-20 and Biogel P-2
Dieter Hackenberg et al.
Plant physiology, 172(2), 1154-1166 (2016-08-24)
In this study, we report the functional characterization of heterotrimeric G-proteins from a nonvascular plant, the moss Physcomitrella patens. In plants, G-proteins have been characterized from only a few angiosperms to date, where their involvement has been shown during regulation
Laura A Moody et al.
The New phytologist, 218(3), 1270-1277 (2018-03-03)
Forward genetics is now straightforward in the moss Physcomitrella patens, and large mutant populations can be screened relatively easily. However, perturbation of development before the formation of gametes currently leaves no route to gene discovery. Somatic hybridization has previously been
D T Kaplan et al.
Journal of nematology, 22(3), 399-406 (1990-07-01)
Radopholus spp. were reared in carrot tissue culture via established procedures, with slight modification. Several plant tissue maceration enzymes and flotation media (salts and sucrose) were evaluated with regard to nematode toxicity and extraction efficiency. Best extraction of viable nematodes
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.