CS0340
Dihydrofolate Reductase Assay Kit
1 kit sufficient for 50-100 tests
Synonym(e):
DHFR Assay Kit
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualitätsniveau
Verwendung
kit sufficient for 50-100 tests
Versandbedingung
dry ice
Lagertemp.
−20°C
Angaben zum Gen
human ... DHFR(1719)
Anwendung
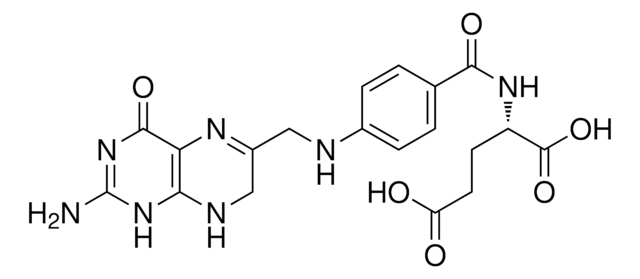
Dihydrofolic acid+NADPH+H+ ↔ Tetrahydrofolic acid+NADP+
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Leistungsmerkmale und Vorteile
- Quick and simple method.
- The kit contains all the reagents required for a colorimetric assay of DHFR activity in cell lysates, tissue homogenates, or column fractions of purified enzyme.
- The kit includes a purified enzyme for use as a positive control and screening of DHFR inhibitors.
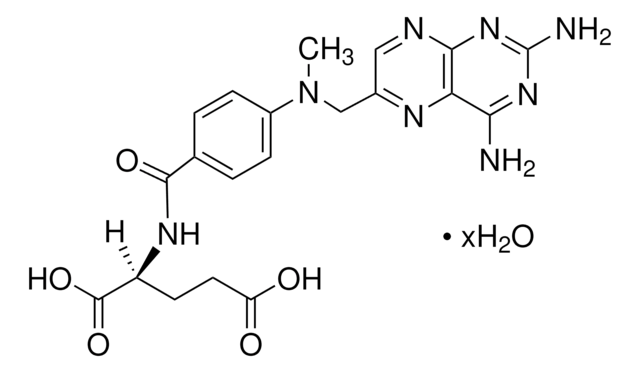
- The kit includes methotrexate (MTX), a prokaryotic and eukaryotic DHFR specific inhibitor, which exhibits anti-tumor activities.
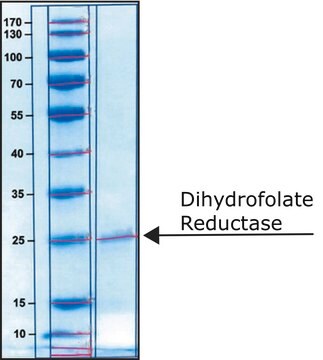
- The kit was tested on A431, NIH-3T3, and CHO cell lines, rat liver, kidney, brain, and skeletal muscle tissue extracts, and recombinant DHFR.
Nur Kit-Komponenten
- Assay Buffer 10x for DHFR 30 mL
- Dihydrofolate Reductase (DHFR) human .1 U
- Dihydrofolic acid (DHFR substrate) 3 x 10
- Amethopterin (+)(methotrexate, MTX)
(DHFR inhibitor) 2 x 10 - NADPH (β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate reduced tetrasodium salt) 25 mg
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Repr. 1B - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Zielorgane
Respiratory system
Lagerklassenschlüssel
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
This article reviews some of our newest and most innovative technologies and their specific applications toward cancer research. It describes how complex the disease of cancer is, and how difficult it is to identify one topic that is completely unrelated to any other.
This issue of Biofiles reviews some of our newest and most innovative technologies and their specific applications toward cancer research. In preparing this issue of Biofiles, one is reminded how complex the disease of cancer is, and how difficult it is to identify one topic that is completely unrelated to any other.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.