T7E1001
T7 Endonuclease Detection Assay
Gene editing analysis kit with T7 endonuclease digestion and detection by SDS-PAGE
Synonym(s):
T7 endonuclease assay
About This Item
Recommended Products
packaging
kit of 6 vials (reagents for 25 Reactions)
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
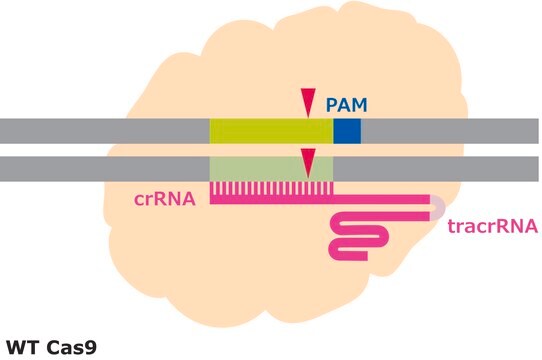
Following a gene editing experiment, genomic DNA surrounding the target locus is amplified by PCR, and the PCR amplicons are denatured and reannealed through heating and slow cooling. If NHEJ events have occurred, then, after reannealing, several products are possible. Homoduplexes can form where a WT strand is reannealead to a WT strand or an indel-carrying strand is reannealed to an indel-carrying strand. Heteroduplexes form when a WT strand is reannealed to an indel-carrying strand causing a mismatch. Heteroduplex products with mismatches are cleaved by the T7 endonuclease. Separating the DNA products after treatment with T7 endonuclease by gel electrophoresis will result in a banding pattern indicative of the amount of heteroduplexes in the sample. The amount of cleaved heteroduplexes is directly related to the amount of indel activity.
Application
Features and Benefits
- Technically simple method based on well-known techniques
- Easily interpretable results
- Fast analysis turnaround
- Cost-effective
Components
- one vial of T7 Endonuclease I
- one vial of Control Template and Primer Mix
- one vial of Buffer solution
- one vial of DNA Ladder - 1KB
- one vial of Gel Loading Dye (6X)
- one vial of Proteinase K
Principle
Efficiency in gene editing can vary in large part due to the target sequences. Chromatin structure and some sequence elements, for example high GC-content, can inhibit editing at some genomic sequences, affecting sgRNA activity. Additionally, favorable bases in the sgRNA sequence such as a guanine proximal to the PAM can promote sgRNA activity, but these preferred bases may not be available at the target site. It is important to evaluate the gene editing ability of several sgRNAs by quantifying the frequency of modifications using a method like T7 endonuclease mismatch detection.
signalword
Danger
hcodes
pcodes
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
After you have performed a CRISPR experiment it is important to determine which gRNAs performed successfully editing. There are many ways to validate CRISPR gene editing experiments. A quick and easy way to check for cutting is by using the Sigma-Aldrich® T7E1 mismatch detection kit.
Protocols
Guaranteed PURedit™ CRISPR synthetic gRNAs and Cas9 protein offer industry-leading on-site cutting and specificity
Related Content
The largest offering of quality Cas9 proteins ensures you have the perfect CRISPR reagents for your specific experimental needs. Rigorous purification, NLS signals, increased specificity and activity ensure your gene editing experiments are efficient and simple.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service