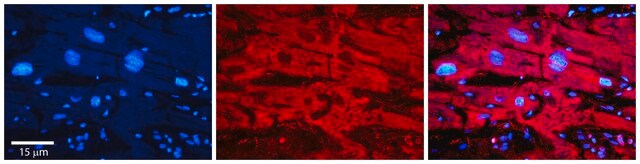
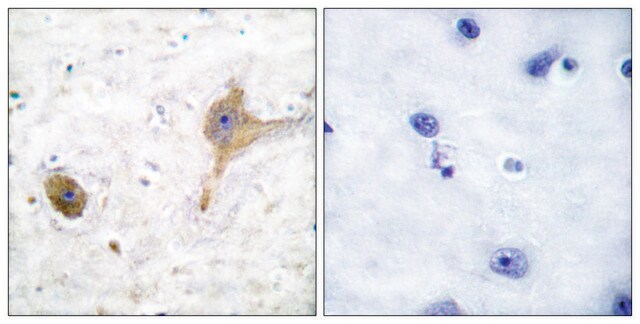
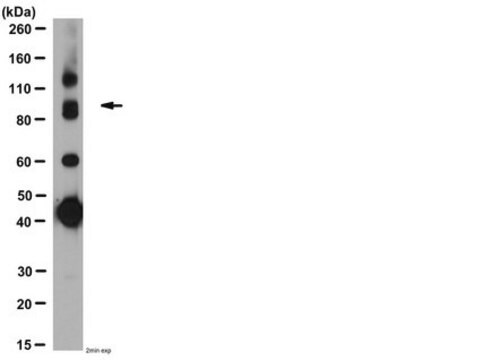
General description
The GABAB receptor (GABABR) is a heteromeric G-protein-coupled receptor. It has two subunits-GABAB1 (γ-aminobutyric acid type B receptor subunit 1) and GABAB2 (γ-aminobutyric acid type B receptor subunit 2). In the hippocampus, GABAB2 is present in dendrites and located in the extra-synaptic membrane of spines and dendritic shafts. This gene is located on rat chromosome 5q.
Immunogen
peptide CKDPIEDINSPEHIQRRLSL corresponding to residues 875-894 of human GABABR2.
Application
Anti-GABAB Receptor 2 antibody produced in rabbit is suitable for western blotting at a working dilution of 1:200 using rat brain membranes.
Anti-GABAB Receptor 2 antibody has been used in western blotting.
Applications in which this antibody has been used successfully, and the associated peer-reviewed papers, are given below.
Western Blotting (1 paper)Biochem/physiol Actions
The inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA signals through two distinct types of pre- and postsynaptic receptors, GABAA and GABAB. Both GABA receptors can regulate depression of synaptic transmission and be involved in the inhibition controlling neuronal excitability. The GABA transmitter interacts with three types of receptors: the ionotropic receptors GABAA and GABAC and the metabotropic GABAB receptor (GABABR). GABABR is a G-protein coupled receptor that plays a key role in slow synaptic inhibition in the brain and spinal cord. GABABR is a heteromer with two subunits, GABABR1 and GABABR2. The amino acids within the second intracellular domain of GABA(B2) are essential for the coupling of GABA(B) receptor heterodimers to their downstream effector systems. The N-termini on both the GB1 and GB2 receptors are involved in the normal coupling of GABAB receptors to their physiological effectors, G(i) and G-protein-activated potassium channels (GIRKs).
Target description
The GABABR2 was shown to be essential for trafficking and G-protein binding, while the GABAB R1 subunit was demonstrated to be important for agonist and antagonist binding. GABABR2 is highly expressed in brain especially at the cerebral cortex, thalamus, hippocampus, and spinal cord and to a lesser extent in testis.
Physical form
Lyophilized from phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 1% BSA and 0.05% sodium azide.
Reconstitution
Reconstitute the lyophilized vial with 50 μL or 200 μL deionized water, depending on package size. Further dilutions should be made using a carrier protein such as BSA (1-3%).
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.