推薦產品
一般說明
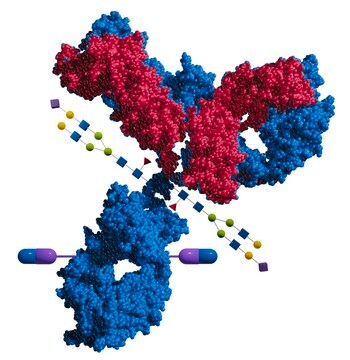
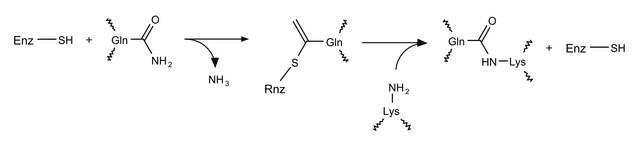
谷氨酰胺转胺酶(TG)是一系列催化异肽键形成的酶。 这一键合形成发生在谷氨酰胺的γ-羧酰胺基团和各种伯胺(主要是赖氨酸的ε-氨基)之间。 所得谷氨酰胺转胺酶分子间或分子内交联高度稳定,并显示出对蛋白水解降解的高抗性。 谷氨酰胺转胺酶交联活性支持血栓、皮肤和头发的形成。另一方面,TG现在被认为与乳糜泻、亨廷顿和帕金森病有关。历史上,微生物谷氨酰胺转胺酶在食品工业中被大量使用。 与哺乳动物相比,微生物TG分子量小且不依赖钙,因此常被用于较新的应用(如位点特异性蛋白修饰和抗体药物偶联)。
應用
微生物谷氨酰胺转胺酶已被用于:
- 蛋白质交联和特定位点标记
- 抗体药物偶联
- 3D生物打印生物油墨制备
- 食品相关免疫原性/致病性相关研究
特點和優勢
- 小型(~38kDa)和钙非依赖性酶
- 高度纯化的冻干酶
- 一致和可再现的活性
- 内毒素含量特征化
準備報告
仅供研发使用。&不可用于药物、家庭或其他用途。有关危险和安全处理方法的信息,请参阅安全数据说明书。
儲存和穩定性
冷冻干燥后的产品保存在-20°C下。建议将重组蛋白保存在-20°C的工作等分中,以避免反复冻融循环。
訊號詞
Danger
危險聲明
危險分類
Resp. Sens. 1
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Matthias Torsten et al.
Frontiers in pediatrics, 6, 389-389 (2019-01-09)
The enzyme microbial transglutaminase is heavily used in the food processing industries to ameliorate food qualities and elongate the products' shelf life. As a protein's glue, it cross-links gliadin peptides, creating neo-complexes that are immunogenic and potentially pathogenic to celiac
Miaomiao Zhou et al.
Biofabrication, 11(2), 025011-025011 (2019-02-12)
Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) is a versatile biomaterial that has been shown to possess many advantages such as good biocompatibility, support for cell growth, tunable mechanical properties, photocurable capability, and low material cost. Due to these superior properties, much research has
Martin Griffin et al.
The Biochemical journal, 368(Pt 2), 377-396 (2002-10-09)
Transglutaminases (Tgases) are a widely distributed group of enzymes that catalyse the post-translational modification of proteins by the formation of isopeptide bonds. This occurs either through protein cross-linking via epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine bonds or through incorporation of primary amines at selected peptide-bound
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務