推薦產品
生物源
rabbit muscle
品質等級
形狀
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
技術
electrophoresis: suitable
UniProt登錄號
異物活動
ATPase Activity ≤0.01 units/mg protein
儲存溫度
−20°C
基因資訊
rabbit ... PBV1SPCR2(100009284)
一般說明
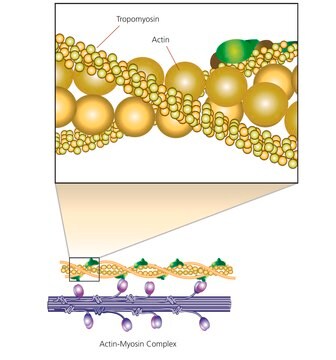
Myosin heavy chain (MHC) is a motor protein of muscle thick filaments. MHC regulates ultrastructural diversity of myofibrils.
應用
Myosin Heavy Chain from rabbit muscle has been used:
- in SDS analysis of myosin heavy chain (MHC) composition and content
- for microinjection into the outflow of heart (blood serum) and the cephalic cavities (embryonic cerebrospinal fluid) of chick embryo
- as a muscle protein, to study the role of ascorbate as a facilitator of glycogen storage in muscles
生化/生理作用
Molecular motor involved in the contraction of muscles.
外觀
Solution in 50% glycerol containing 0.6 M KCl and 0.005 M potassium phosphate, pH 6.5
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
客戶也查看了
L Wells et al.
The EMBO journal, 15(17), 4454-4459 (1996-09-02)
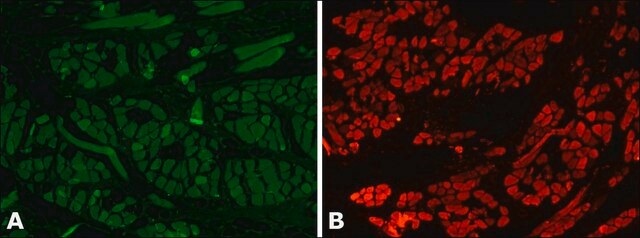
Myosin heavy chain (MHC) is the motor protein of muscle thick filaments. Most organisms produce many muscle MHC isoforms with temporally and spatially regulated expression patterns. This suggests that isoforms of MHC have different characteristics necessary for defining specific muscle
Myosin heavy chain isoforms regulate muscle function but not myofibril assembly.
Wells L, et al.
The Embo Journal, 15(17), 4454-4459 (1996)
Morphological and biochemical alterations of skeletal muscles from the genetically obese (ob/ob) mouse
Kemp JG, et al.
International journal of obesity (2005), 33(8), 831-831 (2009)
I Morano
Journal of molecular medicine (Berlin, Germany), 77(7), 544-555 (1999-09-24)
Cardiac contraction is triggered by the cyclic interaction of the "molecular motor" protein myosin with the actin filament, consuming ATP as the energy source to produce tension or shortening. The myosin heavy chain (MHC) contains the actin- and ATP-binding sites
A blood-CSF barrier function controls embryonic CSF protein composition and homeostasis during early CNS development
Parvas M, et al.
Developmental Biology, 321(1), 51-63 (2008)
文章
Myosins are a family of ATP-dependent motor proteins. Myosin II is the major contractile protein involved in eukaryotic muscle contraction by “walking” along actin microfilaments of the sarcomere
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務