推薦產品
生物源
mouse
品質等級
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
purified immunoglobulin
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
IM-75, monoclonal
形狀
buffered aqueous solution
分子量
antigen ~60 kDa
物種活性
bovine, human, mouse, rat
技術
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
indirect ELISA: suitable
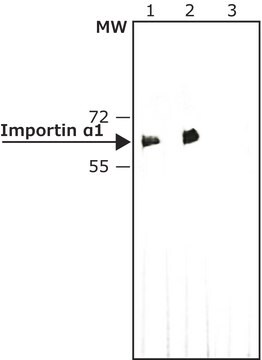
western blot: 1-2 μg/mL using HeLa cell extract
同型
IgG2b
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... KPNA4(3840)
mouse ... Kpna4(16649)
rat ... Kpna4(361959)
一般說明
Monoclonal Anti-Importin α (mouse IgG2b isotype) is derived from the hybridoma IM-75 produced by the fusion of mouse myeloma cells (NS1 cells), and splenocytes from BALB/c mice, immunized with recombinant human importin α. The Importin α family of proteins is comprised of three subfamilies based on amino acid sequence similarity: SRP1-like subfamily (containing the SRP1, importin α5, α6 and α7), Rch1-like subfamily (containing Rch1, pendulin, importin α2), and α3/Qip1-like subfamily (containing α4).
免疫原
recombinant human importin α.
應用
Anti-Importin α antibody, Mouse monoclonal has been used:
- enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- immunoblotting
- immunoprecipitation
- immunocytochemistry
Monoclonal Anti-Importin α antibody produced in mouse has been used in western blotting.
生化/生理作用
The gene KPNA4 (karyopherin subunit α 4) encodes a 16kDa protein, also referred to as importin α 3 belonging to the family of karyopherins (designated KPNA1 to KPNA4). It participates in the recognition of NLS (nuclear localization sequence) sites and dock NLS-containing proteins destined for transport into the nuclear pore complex. It binds to translocon and participates in the sorting of INM (inner nuclear membrane)-directed integral membrane proteins. It associates with nucleoporins and functions in cargo-translocation across the nuclear membrane. Each KPNA contains an N-terminal repeat domain called the importin β binding site that binds to KPNB1, which in turn directs each KPNA/cargo complex through the nuclear pore. The encoded shuttling protein also functions in NF (nuclear factor)-κB nuclear translocation.
外觀
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, and 15 mM sodium azide.
免責聲明
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
未找到適合的產品?
試用我們的產品選擇工具.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
nwg
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Jin Xu et al.
Oncology reports, 30(4), 1878-1882 (2013-08-01)
Recent studies have shown the localization of RhoA in the cell nucleus, in addition to its cellular distribution in the cytosol and cell membrane. Our previous results that a high amount of RhoA was detected in gastric cancer cell nucleus
Guillaume Huet et al.
Journal of cell science, 126(Pt 2), 497-507 (2012-12-04)
Phactr proteins bind actin and protein phosphatase 1 (PP1), and are involved in processes ranging from angiogenesis to cell cycle regulation. Phactrs share a highly conserved RPEL domain with the myocardin-related transcription factor (MRTF) family, where actin binding to this
KPNA4 Mediates Vitamin D-Dependent Inhibition of NF-kB Activity in Swine Epicardial Preadipocytes.
Chen, et al.
Circulation, 130, A12818-A12818 (2014)
Aging impairs transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in human microvascular endothelial cells: implications for angiogenesis and cell survival.
Ahluwalia, A., et al.
Journal of Physiology And Pharmacology, 65 (2014)
Patrick von Morgen et al.
Biology of the cell, 110(6), 137-146 (2018-04-01)
Repair of damaged DNA is essential for maintaining genomic stability. TP53-binding protein 1 (53BP1) plays an important role in repair of the DNA double-strand breaks. Nuclear localisation of 53BP1 depends on importin β and nucleoporin 153, but the type and
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務