推薦產品
產品名稱
激活素 A 人, recombinant, expressed in HEK 293 cells, HumanKine®, suitable for cell culture
生物源
human
品質等級
重組細胞
expressed in HEK 293 cells
化驗
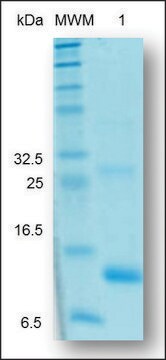
≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
形狀
lyophilized powder
效力
≤5 ng/mL EC50
品質
endotoxin tested
分子量
dimer 25 kDa (non-glycosylated)
包裝
pkg of 5x10 μg
pkg of 10 μg
技術
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
雜質
≤1 EU/mg
儲存溫度
−20°C
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
生化/生理作用
Activin-A participates in a diverse array of functions that include; hypothalamic/pituitary/gonadal hormone secretion, insulin secretion; cell growth, differentiation and survival (apoptosis); embryonic patterning and development; wound healing; and inflammation/immune response. It was initially identified as a follicle stimulating hormone/FSH-releasing protein (gonadal hormone), Ling N, et al. (1986) and erythroid differentiation factor (EDF), Schwall R, et al. (1989). The FSH activity is linked to an increase in the population of pituitary gonadotrophs by Katayama T, et al. (1990). In addition to gonadotrophs, activin-A also modifies somatotrophs and lactotrophs, Kitaoka, et al. (1988).
Activin-A stimulates glycogenolysis in isolated rat hepatocytes, Mine T ET. al. (1989) and elevates insulin release from rat pancreatic islets, Verspohl EJ et al. (1993). Activin-A stimulates insulin secretion in rat pancreatic islets, Totsuka Y, et al. (1988).
Follistatin, an activin-binding protein, is a principle regulator of activin activity, de Winter JP, et al. (1996); however during embryogenesis, Cripto is an important noncompetitive activin antagonist that facilitates Nodal signaling, Kelber JA, et al. (2008).
A role for activin-A as a regulator of cell proliferation was recognized by Gonzalez-Manchon C and Vale W. (1989); wherein Act-A inhibited the growth of and induced morphological changes in CHO-KI cells in culture, in a way similar to but less potent than TGF-β.
Activin A is involved with the entire process of embryo development from germ cells thru embryonic development to adult tissues. It stimulates spermatogonial proliferation in germ-Sertoli cell cocultures, Mather JP, et al. (1990) and is a maturation factor for oocytes, Itoh M, et al. (1990). Activin A promotes proliferation of human luteinized preovulation granulose cells (ovarian granulose cells), Rabinovici J, et al. (1990).
Activin-A stimulates glycogenolysis in isolated rat hepatocytes, Mine T ET. al. (1989) and elevates insulin release from rat pancreatic islets, Verspohl EJ et al. (1993). Activin-A stimulates insulin secretion in rat pancreatic islets, Totsuka Y, et al. (1988).
Follistatin, an activin-binding protein, is a principle regulator of activin activity, de Winter JP, et al. (1996); however during embryogenesis, Cripto is an important noncompetitive activin antagonist that facilitates Nodal signaling, Kelber JA, et al. (2008).
A role for activin-A as a regulator of cell proliferation was recognized by Gonzalez-Manchon C and Vale W. (1989); wherein Act-A inhibited the growth of and induced morphological changes in CHO-KI cells in culture, in a way similar to but less potent than TGF-β.
Activin A is involved with the entire process of embryo development from germ cells thru embryonic development to adult tissues. It stimulates spermatogonial proliferation in germ-Sertoli cell cocultures, Mather JP, et al. (1990) and is a maturation factor for oocytes, Itoh M, et al. (1990). Activin A promotes proliferation of human luteinized preovulation granulose cells (ovarian granulose cells), Rabinovici J, et al. (1990).
分析報告
The specific activity was determined by the dose-dependent inhibition of proliferation of the MPC-11 cell line (mouse plasmocytoma cell line).
法律資訊
HumanKine is a registered trademark of Proteintech Group, Inc. and Humanzyme, Inc
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Yan Li et al.
The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism, 100(11), E1415-E1427 (2015-08-26)
Activin A increases matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 2 expression and cell invasion in human trophoblasts, but whether the expression of MMP2 is essential for the proinvasive effect of activin A has yet to be determined. Moreover, the identity of the activin
Hannah E J Yong et al.
Pregnancy hypertension, 5(4), 346-353 (2015-11-26)
Activin A, a TGFβ family member, circulates in the maternal blood at increasing concentrations throughout gestation during a healthy pregnancy. The circulating concentration of activin A is further increased in pre-eclampsia (PE), a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy that is marked
Xu Qian et al.
Biomaterials, 35(36), 9581-9590 (2014-09-06)
Well-defined culture conditions are essential for realizing the full potential of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) in regenerative medicine where large numbers of cells are required. Synthetic polymers such as poly[2-(methacryloyloxy) ethyl dimethyl-(3-sulfopropyl) ammonium hydroxide] (PMEDSAH), offer multiple advantages over
Melissa L Brown et al.
Islets, 6(5-6), e1017226-e1017226 (2015-04-04)
Emerging evidence suggests that activin with its associated receptors, second messengers, and antagonists would be excellent targets for therapeutic drug development in the treatment of diabetes. We undertook the current study to investigate the ability to extrapolate findings from rodent
Yasuhide Ohinata et al.
PloS one, 9(9), e107308-e107308 (2014-09-10)
The inner cell mass (ICM) and trophoblast cell lineages duet early embryonic development in mammals. After implantation, the ICM forms the embryo proper as well as some extraembryonic tissues, whereas the trophoectoderm (TE) exclusively forms the fetal portion of the
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務