推薦產品
生物源
rabbit
品質等級
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
affinity isolated antibody
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
polyclonal
形狀
buffered aqueous solution
分子量
antigen ~22 kDa
物種活性
rat, hamster, monkey, mouse, bovine, human, canine
濃度
~1 mg/mL
技術
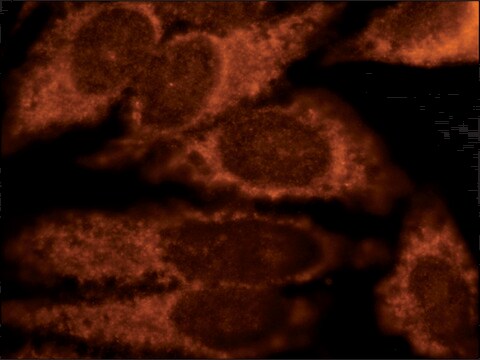
indirect immunofluorescence: 2.5-5 μg/mL using rat NRK cells
western blot (chemiluminescent): 0.2-0.4 μg/mL using whole extract of human HeLa and mouse 3T3 cells.
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... DERL1(79139)
mouse ... Derl1(67819)
一般說明
Derlin-1 is a 22kDa hydrophobic protein that spans the lipid bilayer of the ER four times with its amino- and carboxy-terminus in the cytosol. It is expressed with high levels in liver, spleen, pancreas, lung, thymus, and ovary.
Derlin-1 shares human homology with yeast Der1p.
免疫原
a synthetic peptide corresponding to the C-terminal region of human Derlin-1 with N-terminal added cysteine, conjugated to KLH. The corresponding sequence is identical in mouse.
應用
Anti-Derlin-1 antibody produced in rabbit has been used in:
- immunostaining
- co-immunoprecipitation
- immunofluorescence
生化/生理作用
Derlin-1 can interact with peptide:N-glycanase (PNGase), a deglycosylating enzyme, bringing it close to misfolding dislocating glycoproteins.
Derlin-1 is required for the dislocation of misfolded proteins from the ER lumen to the cytosol, where they are destroyed by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. It interacts with PNGase, a deglycosylating enzyme, bringing it close to misfolding dislocating glycoproteins. It forms a membrane protein complex with VIMP ( (VCP-interacting membrane protein) and this complex serves as a receptor for p97. p97 interacts with several ubiquitin ligases, thus recruiting them to Derlin-1.
外觀
0.01M 磷酸缓冲盐溶液,pH 7.4,含 15mM 叠氮化钠。
免責聲明
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
未找到適合的產品?
試用我們的產品選擇工具.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
Zlatka Kostova et al.
The EMBO journal, 22(10), 2309-2317 (2003-05-14)
The surveillance of the structural fidelity of the proteome is of utmost importance to all cells. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the organelle responsible for proper folding and delivery of proteins to the secretory pathway. It contains a sophisticated protein
Molecular characterization and expression of DERL1 in bovine ovarian follicles and corpora lutea
Ndiaye K, et al.
Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology, 8(1), 94-94 (2010)
Yihong Ye et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(40), 14132-14138 (2005-09-28)
Misfolded proteins are eliminated from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by retrotranslocation into the cytosol, a pathway hijacked by certain viruses to destroy MHC class I heavy chains. The translocation of polypeptides across the ER membrane requires their polyubiquitination and subsequent
Yihong Ye et al.
Nature, 429(6994), 841-847 (2004-06-25)
Elimination of misfolded proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by retro-translocation is an important physiological adaptation to ER stress. This process requires recognition of a substrate in the ER lumen and its subsequent movement through the membrane by the cytosolic
Brendan N Lilley et al.
Nature, 429(6994), 834-840 (2004-06-25)
After insertion into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), proteins that fail to fold there are destroyed. Through a process termed dislocation such misfolded proteins arrive in the cytosol, where ubiquitination, deglycosylation and finally proteasomal proteolysis dispense with the unwanted polypeptides. The
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務