推薦產品
產品線
BioReagent
化驗
≥95% (HPLC)
形狀
powder
技術
cell culture | plant: suitable
mp
150-160 °C (dec.) (lit.)
應用
agriculture
SMILES 字串
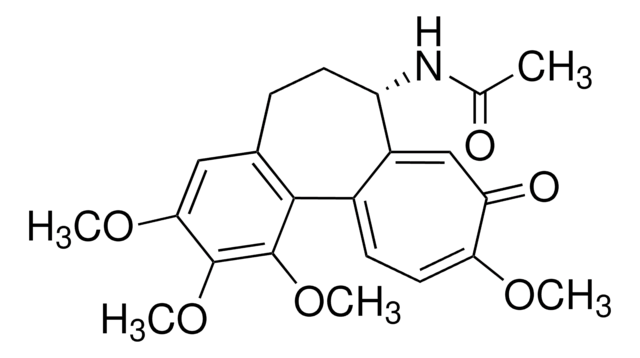
COC1=CC=C2C(=CC1=O)[C@H](CCc3cc(OC)c(OC)c(OC)c23)NC(C)=O
InChI
1S/C22H25NO6/c1-12(24)23-16-8-6-13-10-19(27-3)21(28-4)22(29-5)20(13)14-7-9-18(26-2)17(25)11-15(14)16/h7,9-11,16H,6,8H2,1-5H3,(H,23,24)/t16-/m0/s1
InChI 密鑰
IAKHMKGGTNLKSZ-INIZCTEOSA-N
基因資訊
human ... ABCB1(5243) , CYP3A4(1576) , TUBA1A(7846) , TUBA1B(10376) , TUBA1C(84790) , TUBA3C(7278) , TUBA3E(112714) , TUBA4A(7277) , TUBB(203068) , TUBB1(81027) , TUBB2A(7280) , TUBB2B(347733) , TUBB3(10381) , TUBB4A(10382) , TUBB4B(10383) , TUBB6(84617) , TUBB8(347688)
mouse ... Abcb1a(18671) , Abcb1b(18669)
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
一般說明
應用
- 用作骨髓巨噬细胞中的微管蛋白聚合抑制剂
- 用于抑制人神经元细胞体外神经突生长
- 用作微管去稳定剂,在诱导多能干细胞分化神经元中诱导周围神经病变
生化/生理作用
準備報告
訊號詞
Danger
危險聲明
危險分類
Acute Tox. 2 Oral - Muta. 1B
儲存類別代碼
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
分析證明 (COA)
輸入產品批次/批號來搜索 分析證明 (COA)。在產品’s標籤上找到批次和批號,寫有 ‘Lot’或‘Batch’.。
客戶也查看了
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務