推薦產品
等級
pharmaceutical primary standard
API 家族
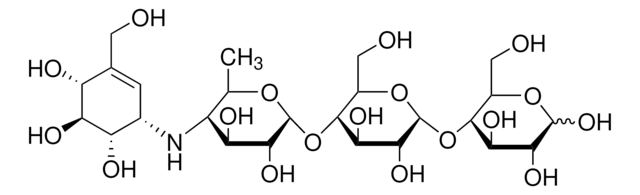
acarbose
製造商/商標名
EDQM
應用
pharmaceutical (small molecule)
格式
neat
儲存溫度
2-8°C
SMILES 字串
C[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[C@@H]2CO)O[C@H]3[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)O[C@@H]3CO)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1N[C@H]4C=C(CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]4O
InChI
1S/C25H43NO18/c1-6-11(26-8-2-7(3-27)12(30)15(33)13(8)31)14(32)19(37)24(40-6)43-22-10(5-29)42-25(20(38)17(22)35)44-21-9(4-28)41-23(39)18(36)16(21)34/h2,6,8-39H,3-5H2,1H3/t6-,8+,9-,10-,11-,12-,13+,14+,15+,16-,17-,18-,19-,20-,21-,22-,23-,24-,25-/m1/s1
InChI 密鑰
XUFXOAAUWZOOIT-SXARVLRPSA-N
基因資訊
human ... AMY2A(279) , MGAM(8972)
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
一般說明
This product is provided as delivered and specified by the issuing Pharmacopoeia. All information provided in support of this product, including SDS and any product information leaflets have been developed and issued under the Authority of the issuing Pharmacopoeia.For further information and support please go to the website of the issuing Pharmacopoeia.
應用
Acarbose for identification EP Reference standard, intended for use in laboratory tests only as specifically prescribed in the European Pharmacopoeia.
生化/生理作用
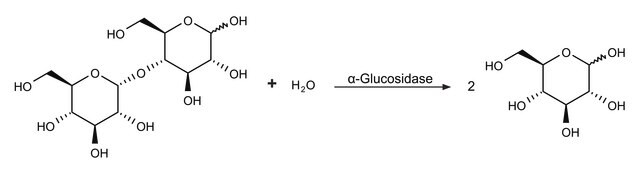
作为可逆性α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂的改性四糖。
包裝
The product is delivered as supplied by the issuing Pharmacopoeia. For the current unit quantity, please visit the EDQM reference substance catalogue.
其他說明
Sales restrictions may apply.
相關產品
產品號碼
描述
訂價
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Uwe Zeymer
International journal of cardiology, 107(1), 11-20 (2005-12-13)
Impaired glucose metabolism is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events and cardiovascular-associated mortality. Postprandial hyperglycaemia is one of the earliest identifiable indicators of impaired glucose control. It contributes to the progression from impaired glucose tolerance to overt type
Sho-ichi Yamagishi et al.
Current drug metabolism, 10(2), 159-163 (2009-03-12)
Diabetes is associated with an increase risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Recently, macrovascular complications of diabetes have been shown to start before the development of diabetes. Indeed, several clinical studies have confirmed the increased risk of CVD in patients with
Giuseppe Derosa et al.
Clinical therapeutics, 34(6), 1221-1236 (2012-05-09)
Epidemiologic studies have revealed that postprandial hyperglycemia significantly contributes to high glycated hemoglobin concentrations and could be linked to the development of chronic diabetic complications. The purpose of our review was to evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety profile of
Markolf Hanefeld et al.
Cardiovascular drugs and therapy, 22(3), 225-231 (2008-03-01)
Excessive postprandial (pp) glucose excursion in people with IGT and type 2 diabetes is associated with a cascade of proatherogenic events. Acarbose, a potent competitive inhibitor of alpha-glucosidases of the small intestine specifically reduces pp hyperglycemia with an average reduction
Markolf Hanefeld
Cardiovascular diabetology, 6, 20-20 (2007-08-19)
Dysglycaemic disease is one of the most important health issues facing the world in the 21st century. Patients with type 2 diabetes and individuals with prediabetes are at risk of developing macrovascular and microvascular complications. Long-term management strategies are therefore
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務