推薦產品
product name
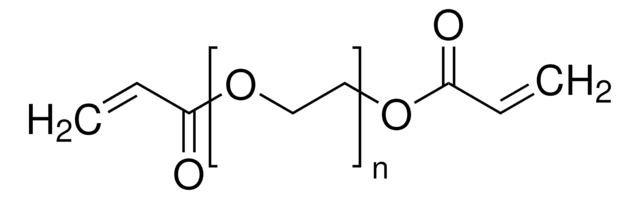
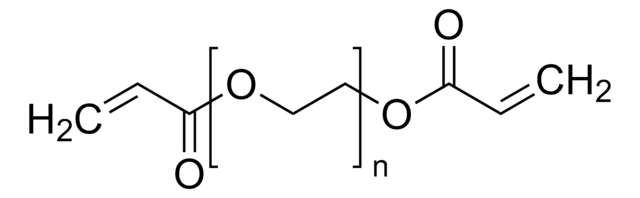
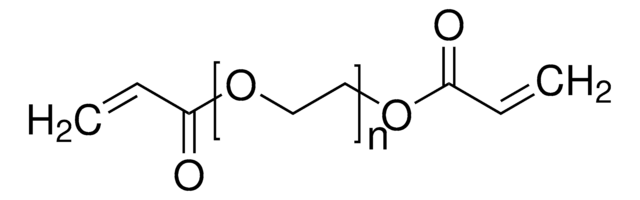
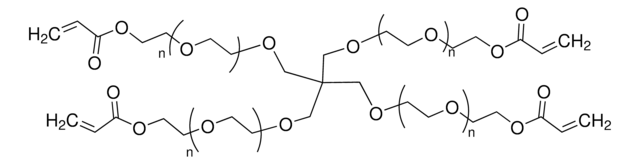
聚(乙二醇)二丙烯酸酯, average Mn 6,000, contains ≤1500 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor
形狀
solid
品質等級
分子量
average Mn 6,000
包含
≤1500 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor
反應適用性
reagent type: cross-linking reagent
reaction type: Polymerization Reactions
轉變溫度
Tm 59-63 °C
Ω-end
acrylate
α-end
acrylate
聚合物結構
shape: linear
functionality: homobifunctional
儲存溫度
−20°C
SMILES 字串
OCCO.OC(=O)C=C
InChI
1S/C8H10O4/c1-3-7(9)11-5-6-12-8(10)4-2/h3-4H,1-2,5-6H2
InChI 密鑰
KUDUQBURMYMBIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
一般說明
應用
它还可被用作 合金剂用于制备用于气体分离的聚合物膜。 比如,聚(醚嵌段酰胺)/PEGDA共混物膜可被 用于分离CO2/H2.
它还可被用作前体,制备用于柔性锂离子电池的聚合物电解质膜。添加PEGDA增强了离子传导,热稳定性和PEMs的机械韧性。
特點和優勢
- 高 亲水性
- 无毒
- 生物相容
- 非免疫原性
訊號詞
Danger
危險聲明
危險分類
Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
客戶也查看了
文章
Patterning of PEG-based Hydrogels - Engineering Spatial Complexity
In the past two decades, tissue engineering and regenerative medicine have become important interdisciplinary fields that span biology, chemistry, engineering, and medicine.
Progress in biotechnology fields such as tissue engineering and drug delivery is accompanied by an increasing demand for diverse functional biomaterials. One class of biomaterials that has been the subject of intense research interest is hydrogels, because they closely mimic the natural environment of cells, both chemically and physically and therefore can be used as support to grow cells. This article specifically discusses poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels, which are good for biological applications because they do not generally elicit an immune response. PEGs offer a readily available, easy to modify polymer for widespread use in hydrogel fabrication, including 2D and 3D scaffold for tissue culture. The degradable linkages also enable a variety of applications for release of therapeutic agents.
Devising biomaterial scaffolds that are capable of recapitulating critical aspects of the complex extracellular nature of living tissues in a threedimensional (3D) fashion is a challenging requirement in the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務