About This Item
推薦產品
品質等級
化驗
≥98% trace metals basis
形狀
nanopowder
粒徑
<50 nm (APS)
密度
5.368 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
體積密度
0.89 g/mL
應用
battery manufacturing
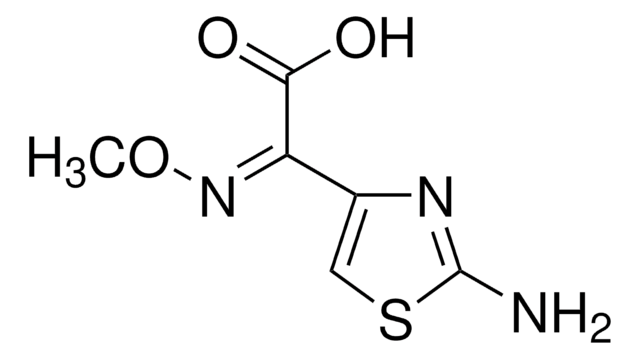
SMILES 字串
O=[Ni].O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O
InChI
1S/2Fe.Ni.4O
InChI 密鑰
NQNBVCBUOCNRFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
一般說明
應用
- fabrication of magnetic nanofiber for data storage and transfer
- electrocatalysts for the splitting of alkaline water
- formation of composite nanofibers for efficient water oxidation electrocatalysis
外觀
訊號詞
Warning
危險聲明
危險分類
Skin Sens. 1
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
客戶也查看了
文章
Currently, magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are attracting a lot of attention because of the possibility of many novel applications, especially in biomedical research.
Professor Hui Mao explores the use of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (INOPs) that offer an alternate contrast-enhancing mechanism.
Magnetic materials permeate numerous daily activities in our lives. They are essential components of a diversity of products including hard drives that reliably store information on our computers, decorative magnets that keep the shopping list attached to the refrigerator door, electric bicycles that speed our commute to work, as well as wind turbines for conversion of wind energy to electrical power.
The application of magnetism and magnetic materials pervades our modern civilization in the form of electrical power, communications and information storage.
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務

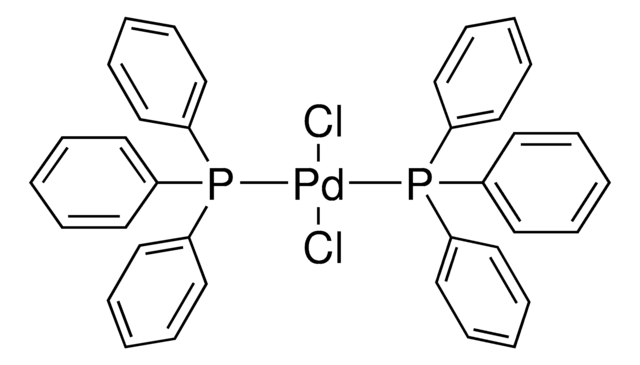
![[1,1′-双(二苯基膦)二茂铁]二氯化钯(II)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/130/734/8846aa26-1858-458a-998d-8c306c13bf0f/640/8846aa26-1858-458a-998d-8c306c13bf0f.png)


![[1,1′-双(二苯基膦)二茂铁]二氯化钯(II)二氯甲烷络合物](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/825/986/4317978b-1256-4c82-ab74-6a6a3ef948b1/640/4317978b-1256-4c82-ab74-6a6a3ef948b1.png)