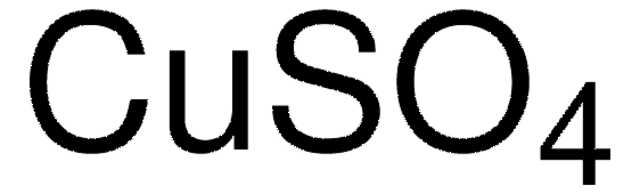推薦產品
等級
for analytical purposes
化驗
99.999% trace metals basis
形狀
powder
反應適用性
reagent type: catalyst
core: copper
雜質
≤15.0 ppm Trace Metal Analysis
mp
620 °C (lit.)
密度
3.386 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
應用
battery manufacturing
SMILES 字串
Cl[Cu]Cl
InChI
1S/2ClH.Cu/h2*1H;/q;;+2/p-2
InChI 密鑰
ORTQZVOHEJQUHG-UHFFFAOYSA-L
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
一般說明
應用
訊號詞
Danger
危險分類
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2
儲存類別代碼
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
客戶也查看了
文章
Noble-Metal Nanostructures with Controlled Morphologies
Oxidation and reduction reactions are some of the most common transformations encountered in organic synthesis, and are some of the organic chemist’s most powerful tools for creating novel products. Below is a list of the most commonly used oxidizing and reducing agents currently available in our catalog.
Oxidation and reduction reactions are some of the most common transformations encountered in organic synthesis
We presents an article about a micro review of reversible addition/fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. RAFT (Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
條款
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about the typical procedures for polymerizing via ATRP, which demonstrates that in the following two procedures describe two ATRP polymerization reactions as performed by Prof. Dave Hadddleton′s research group at the University of Warwick.
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務