所有图片(1)
About This Item
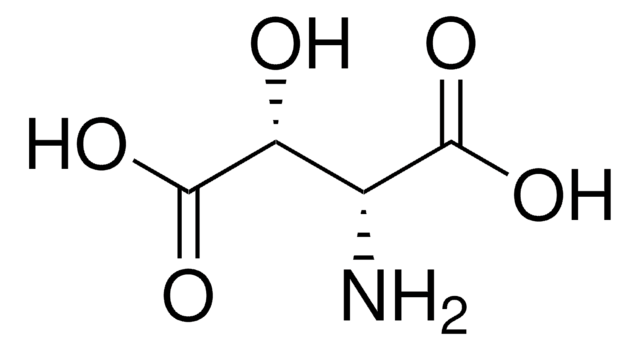
经验公式(希尔记法):
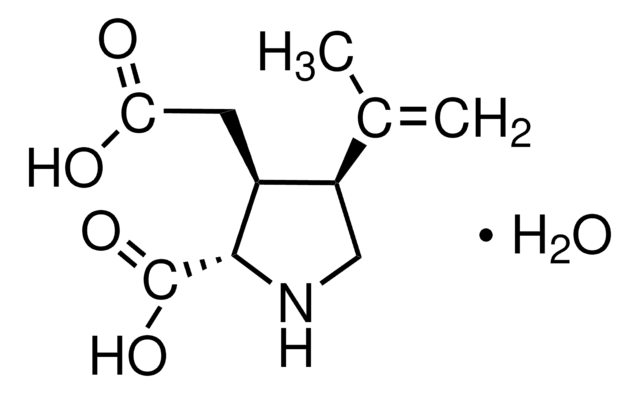
C10H15NO4 · H2O
CAS号:
分子量:
231.25
MDL號碼:
分類程式碼代碼:
12352106
PubChem物質ID:
NACRES:
NA.77
推荐产品
生物源
Digenea simplex
化驗
≥98% (HPLC)
形狀
powder
顏色
white
溶解度
H2O: >10 mg/mL
儲存溫度
2-8°C
SMILES 字串
O.CC(=C)[C@H]1CN[C@@H]([C@H]1CC(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C10H15NO4.H2O/c1-5(2)7-4-11-9(10(14)15)6(7)3-8(12)13;/h6-7,9,11H,1,3-4H2,2H3,(H,12,13)(H,14,15);1H2/t6-,7+,9-;/m0./s1
InChI 密鑰
FZNZRJRSYLQHLT-SLGZUKMRSA-N
正在寻找类似产品? 访问 产品对比指南
應用
红藻氨酸一水合物曾被用于:
- 作为惊厥剂诱发小鼠癫痫发生和癫痫。
- 体外刺激 内毛细胞上螺旋神经节神经元的兴奋性毒性创伤。
- 诱导大鼠癫痫发作模型。
- 诱导成年雄性 Wistar 大鼠癫痫持续状态。
生化/生理作用
离子型谷氨酸受体形成离子通道,并传导 Na + 和 K + 通量。受体具有激动剂结合站点,当激动剂与受体结合后,受体构象更改。红藻氨酸门控通道参与谷氨酸诱导的兴奋性突触后神经元电位。
红藻氨酸-水合物是一种激动剂,属于红藻类离子性谷氨酸受体,在 体内 诱导癫痫发作和神经退行性变,被用于诱导啮齿类动物实验性癫痫,并研究兴奋性诱导神经元凋亡的机制。
相關產品
产品编号
说明
价格
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Functional role of neurotrophin-3 in synapse regeneration by spiral ganglion neurons on inner hair cells after excitotoxic trauma in vitro
Wang Q and Green SH
The Journal of Neuroscience, 31(21), 7938-7949 (2011)
Basic Neurochemistry: Molecular, Cellular and Medical Aspects. (2005)
David P D Woldbye et al.
Brain : a journal of neurology, 133(9), 2778-2788 (2010-08-07)
Gene therapy using recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors overexpressing neuropeptide Y in the hippocampus exerts seizure-suppressant effects in rodent epilepsy models and is currently considered for clinical application in patients with intractable mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Seizure suppression by neuropeptide Y
Diffusion tensor MRI of axonal plasticity in the rat hippocampus
Laitinen T, et al.
Neuroimage, 51(2), 521-530 (2010)
Carlos G Martinez-Moreno et al.
International journal of molecular sciences, 20(18) (2019-09-13)
In addition to its role as an endocrine messenger, growth hormone (GH) also acts as a neurotrophic factor in the central nervous system (CNS), whose effects are involved in neuroprotection, axonal growth, and synaptogenic modulation. An increasing amount of clinical
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门