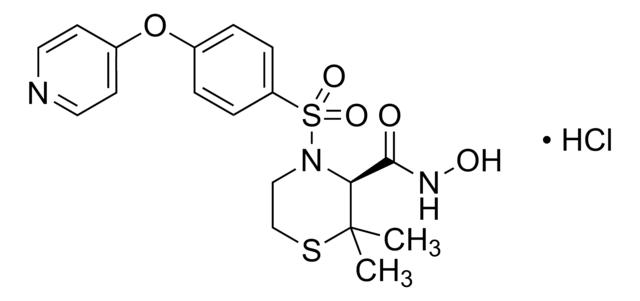
SML1285
Febuxostat
98.5-102.0% (dry basis), powder, xanthine oxidase inhibitor
Synonym(s):
2-(3-Cyano-4-isobutoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxylic acid, Adenuric, Atenuri, Uloric
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C16H16N2O3S
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
316.37
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
51111800
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.77
Recommended Products
Product Name
Febuxostat, 98.5-102.0%
Quality Level
assay
98.5-102.0%
form
powder
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
CC(C)COC1=C(C#N)C=C(C2=NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)S2)C=C1
InChI
1S/C16H16N2O3S/c1-9(2)8-21-13-5-4-11(6-12(13)7-17)15-18-10(3)14(22-15)16(19)20/h4-6,9H,8H2,1-3H3,(H,19,20)
InChI key
BQSJTQLCZDPROO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
General description
Febuxostat is a potent, non-purine compound, which inhibits the expression of cytokines/chemokines. It has also been reported to inhibit LPS-induced TNF-α, VCAM-1, MMP9 and MCP-1 expression.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Febuxostat is a potent non-purine xanithine oxidase inhibitor.
Febuxostat is a potent non-purine xanithine oxidase inhibitor. Febuxostat is used in urate lowering therapies (ULTs) for the treatment of gout.
Caution
Freely soluble in N,N-dimethyl formamide, Soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide, sparingly soluble in ethanol or trichloromethane, slightly soluble in methanol, practically insoluble in water
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Johji Nomura et al.
PloS one, 8(9), e75527-e75527 (2013-10-03)
Excess reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation can trigger various pathological conditions such as inflammation, in which xanthine oxidase (XO) is one major enzymatic source of ROS. Although XO has been reported to play essential roles in inflammatory conditions, the molecular
Yoshiro Tanaka et al.
Free radical biology & medicine, 162, 298-308 (2021-01-21)
Accumulating evidence suggests that high serum uric acid (UA) is associated with left ventricular (LV) dysfunction. Although xanthine oxidase (XO) activation is a critical regulatory mechanism of the terminal step in ATP and purine degradation, the pathophysiological role of cardiac
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service