SAE0147
Thrombin protease, biotin-tagged
human recombinant,expressed in HEK 293 cells, ≥5000 units/mL
Synonym(s):
Factor IIa, fibrinogenase, thrombase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.77
Recommended Products
biological source
human
recombinant
expressed in HEK 293 cells
concentration
≥5000 units/mL
technique(s)
protein extraction: suitable
suitability
suitable for additive or modifier in the separation of proteins or peptides
application(s)
life science and biopharma
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
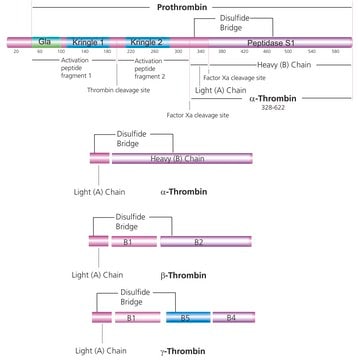
Thrombin is an endolytic serine protease that selectively cleaves the Arg–Gly bonds of fibrinogen to form fibrin and release fibrinopeptides A and B.1,2
The optimal cleavage sites for thrombin are as follows:
1. A-B-Pro-Arg-||-X-Y, where A and B are hydrophobic amino acids, and X and Y are nonacidic amino acids.
2. Gly-Arg-||-Gly
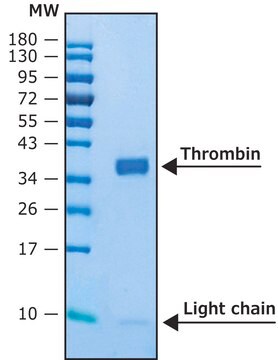
Recombinant human thrombin protease is expressed in human HEK 293 cells as a glycoprotein heterodimer. The DTT-reduced protein migrates as two bands of ∼31 kDa (heavy chain) and ∼6 kDa (light chain) on SDS-PAGE. This protein is manufactured in human cells, with no serum. The human cells expression system allows human-like glycosylation and folding, and often supports higher activity of the protein.
This thrombin protease is useful for cleaving recombinant proteins that are expressed as fusion proteins with this sequence between the carrier domain and the protein of interest.
The optimal cleavage sites for thrombin are as follows:
1. A-B-Pro-Arg-||-X-Y, where A and B are hydrophobic amino acids, and X and Y are nonacidic amino acids.
2. Gly-Arg-||-Gly
Recombinant human thrombin protease is expressed in human HEK 293 cells as a glycoprotein heterodimer. The DTT-reduced protein migrates as two bands of ∼31 kDa (heavy chain) and ∼6 kDa (light chain) on SDS-PAGE. This protein is manufactured in human cells, with no serum. The human cells expression system allows human-like glycosylation and folding, and often supports higher activity of the protein.
This thrombin protease is useful for cleaving recombinant proteins that are expressed as fusion proteins with this sequence between the carrier domain and the protein of interest.
Application
This biotinylated thrombin protease can be used for on-column cleavage of fusion proteins with a thrombin cleavage site. It specifically cleaves the protein of interest from a column-bound fusion protein, leaving the fusion domain or tag bound to the affinity column (e.g., Ni-NTA column) and eluting only the protein of interest.
This method is advantageous over post-elution cleavage for several reasons:
This method is advantageous over post-elution cleavage for several reasons:
- It eliminates most impurities normally associated with purification on Ni-chelating columns.
- It allows gentler elution conditions, with added flexibility in the elution buffer composition. This can mitigate protein aggregation and inactivation.
Features and Benefits
The product is supplied in an aqueous buffer of pH 6.0, with 50% (v/v) glycerol.
Catalytic pH range:11.5–10
Optimal pH:11-8.3
(Note: thrombin precipitates at pH ≤5)
Molecular mass:4,12 37.4 kDa
Human isozymes pI range:6.35–7.6
E280 (1%):12 -18.3
Catalytic pH range:11.5–10
Optimal pH:11-8.3
(Note: thrombin precipitates at pH ≤5)
Molecular mass:4,12 37.4 kDa
Human isozymes pI range:6.35–7.6
E280 (1%):12 -18.3
This Thrombin protease, biotin-tagged enables on-column cleavage of fusion proteins with a thrombin cleavage site.
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service