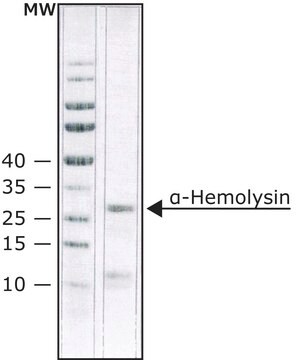
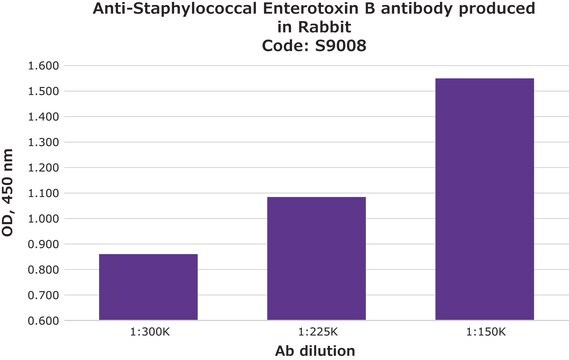
P3838
Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus
Soluble, Cowan Strain, essentially salt-free, lyophilized powder
Synonym(s):
Protein A, Staphylococcus aureus Protein A
About This Item
Recommended Products
conjugate
unconjugated
Quality Level
form
essentially salt-free, lyophilized powder
technique(s)
ELISA: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
western blot: suitable
capacity
7-14 mg/mg, solid binding capacity (human IgG)
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
2-8°C
Gene Information
Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus NCTC 8325 ... SAOUHSC_00069(3919448)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Protein A also participates in a number of different protective biological functions including anti-tumor, toxic, and carcinogenic activities. In addition to acting as an immunomodulator, it also has antifungal and antiparasitic properties.
Preparation Note
Disclaimer
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service