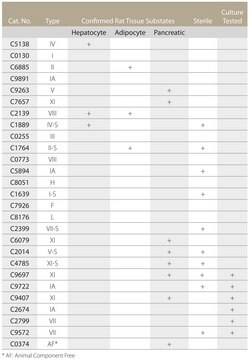
C5894
Collagenase from Clostridium histolyticum
non-sterile; 0.2 μm filtered, Type IA-S, 0.5-5.0 FALGPA units/mg solid, ≥125 CDU/mg solid
Synonym(s):
Clostridiopeptidase A
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
sterility
non-sterile; 0.2 μm filtered
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
≥125 CDU/mg solid
0.5-5.0 FALGPA units/mg solid
mol wt
68-130 kDa
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
Collagenase has been used in the preparation of arterial tissue for the study of Advanced Glycosylation End Products (AGE). The enzyme has also been used along with other proteases for the disaggregation of human tumor, mouse kidney, human brain, lung epithelium and many other tissues. It is also used for liver and kidney perfusion studies, digestion of pancreas, and isolation of nonparenchymal hepatocytes. This enzyme is tested for the release of hepatocytes at approx.1 mg/mL conc. (in a total volume of 100 mL for each rat liver).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Collagenase is activated by four gram atom calcium per mole enzyme. It is inhibited by ethylene glycol-bis(beta-aminoethyl ether) - N, N, N′,N′-tetraacetic acid, beta-mercaptoethanol, glutathione, thioglycolic acid and 8-hydroxyquinoline.
Effective release of cells from tissue requires the action of collagenase enzymes and the neutral protease. Collagenase is activated by four gram atom calcium (Ca2+) per mole enzyme. The culture filtrate is thought to contain at least 7 different proteases ranging in molecular weight from 68-130 kDa. The pH optimum is 6.3-8.8. The enzyme is typically used to digest the connective components in tissue samples to liberate individual cells. Collagenase treatment can cause some cells to die. Typically, concentrations varying from 0.1 to 5 mg/mL are used for digestion. The duration of reaction varyies from 15 minutes to several hours and yields a satisfactory cell dissociation without causing too much cell death. Krebs Ringer buffer with calcium and BSA is preferred and Zn2+ is required for activity.
Caution
As supplied, this product is stable for one year at -20°C. There is no loss in FALGPA or protease activity in 30 days at 37°C, 50°C and -20°C. Solutions of crude collagenase are stable if frozen quickly in aliquots (at 10 mg/mL) and kept frozen at -20°C. Further freeze-thaw cycles will damage the solution. The product retains 100% activity over 7 hours when held on ice.
Unit Definition
One collagen digestion unit (CDU) liberates peptides from collagen from bovine achilles tendon equivalent in ninhydrin color to 1.0 μmole of leucine in 5 hours at pH 7.4 at 37 °C in the presence of calcium ions. One FALGPA hydrolysis unit hydrolyzes 1.0 μmole of furylacryloyl-Leu-Gly-Pro-Ala per min at 25°C. One Neutral Protease unit hydrolyzes casein to produce color equivalent to 1.0 μmole of tyrosine per 5 hr at pH 7.5 at 37°C. One Clostripain Unit hydrolyzes 1.0 μmole of BAEE per min at pH 7.6 at 25°C in the presence of DTT.
Preparation Note
Solutions are typically prepared at 1-2 mg/mL in TESCA buffer (containing 50 mM TES, 0.36 mM Calcium chloride, pH 7.4 at 37°C.
substrate
Product No.
Description
Pricing
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Laura Rennert et al.
Frontiers in immunology, 9, 1589-1589 (2018-08-01)
Endogenously released adenosine-5'-triphosphate (ATP) is a key regulator of physiological function and inflammatory responses in the kidney. Genetic or pharmacological inhibition of purinergic receptors has been linked to attenuation of inflammatory disorders and hence constitutes promising new avenues for halting
Amit P Bhole et al.
Philosophical transactions. Series A, Mathematical, physical, and engineering sciences, 367(1902), 3339-3362 (2009-08-07)
There has been great interest in understanding the methods by which collagen-based load-bearing tissue is constructed, grown and maintained in vertebrate animals. To date, the responsibility for this process has largely been placed with mesenchymal fibroblastic cells that are thought
Aurélie Formey et al.
Cell and tissue research, 343(3), 509-519 (2011-01-19)
Cells with irregular shapes, numerous long thin filaments, and morphological similarities to the gastrointestinal interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) have been observed in the wall of some blood vessels. These ICC-like cells (ICC-LCs) do not correspond to the other cell
Juliana T Y Lee et al.
Journal of orthopaedic research : official publication of the Orthopaedic Research Society, 33(12), 1743-1755 (2015-06-04)
Differences in matrix compositions in human nucleus pulposus (NP) clinical samples demand different cell isolation protocols for optimal results but there is no clear guide about this to date. Sub-optimal protocols may result in low cell yield, limited reliability of
Mako Kato et al.
International journal of pharmaceutics, 423(2), 428-434 (2011-12-27)
Elevated interstitial fluid pressure (IFP) in a tumor is a barrier to tumor accumulation of systemic delivery of nanocarriers. In this study, we investigated whether intravenous injection of type I collagenase (collagenase-1) reduced IFP in tumors and increased the accumulation
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service