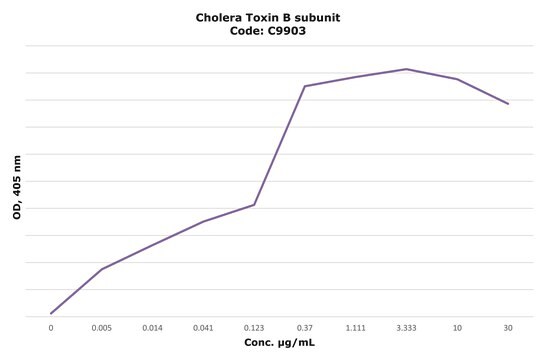
Recommended Products
form
solid
Quality Level
mol wt
~12 kDa
color
white
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
CCOc1ccccc1C(=O)Nc2ccc(Cl)c(c2)C(F)(F)F
InChI
1S/C16H13ClF3NO2/c1-2-23-14-6-4-3-5-11(14)15(22)21-10-7-8-13(17)12(9-10)16(18,19)20/h3-9H,2H2,1H3,(H,21,22)
InChI key
YDXZSNHARVUYNM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Cholera Toxin B subunit is secreted by Vibrio cholerae. It is a pentamer and is nontoxic in nature.
Application
Cholera Toxin B subunit has been used as a tracer to study the ascending projections of the nuclei of the descending trigeminal tract (nTTD) in the zebra finch.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cholera Toxin B subunit stimulates both systemic and mucosal antibody production in animals and humans. CTB functions as an oral subunit vaccine for cholera, which is associated with acute watery diarrhoea.
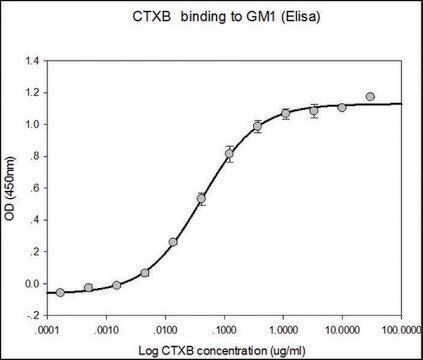
The cholera toxin B subunit is used for track tracing in neurological research, taking advantage of GM1 ganglioside binding and retrograde transport. Tissue culture cells treated with cholera toxin are not killed and tissues of animals do not become necrotic.
Caution
Do not freeze.
Reconstitution
When reconstituted in 0.25 mL distilled water, the compound contains 500 μg of protein in 0.01 M sodium phosphate at pH 7.5.
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Efficacy of a food plant-based oral cholera toxin B subunit vaccine
Arakawa T, et al.
Nature Biotechnology, 16(3), 292-292 (1998)
J Holmgren et al.
Journal of general microbiology, 86(1), 49-65 (1975-01-01)
Structural analysis of cholera toxin by sodium dodecylsulphate polyacrylamide electrophoresis demonstrated two types of non-covalentyly linked subunits, heavy (H) AND LIGHT (L), with respective molecular weights 28000 and 800 to 9000. The H:L protein ratio was I:2, indicating that the
Gangliosides as membrane receptors for tetanus toxincholera toxin and serotonin.
van Heyningen, et al.
Nature, 249, 415-417 (1974)
The ascending projections of the nuclei of the descending trigeminal tract (nTTD) in the zebra finch (Taeniopygia guttata)
Faunes M, et al.
The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 525(5), 2832-2846 (2017)
Expression of the native cholera toxin B subunit gene and assembly as functional oligomers in transgenic tobacco chloroplasts1
Daniell H, et al.
Journal of Molecular Biology, 311(5), 1001-1009 (2001)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service