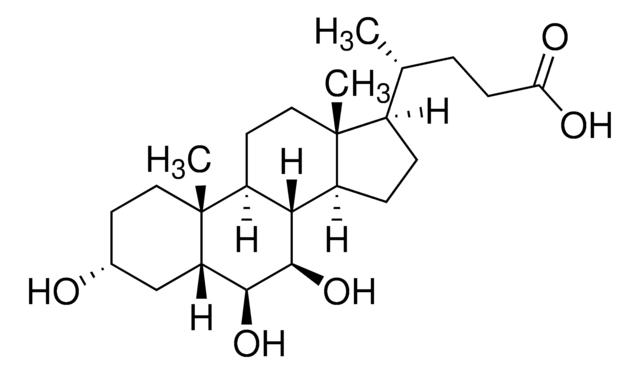
06863
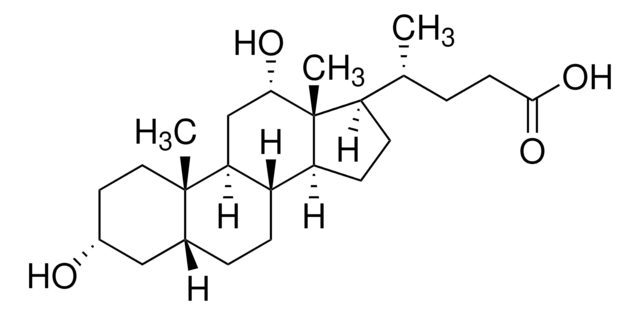
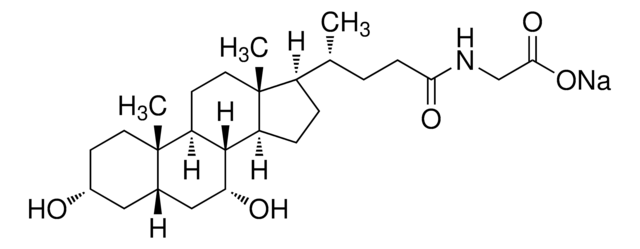
Glycoursodeoxycholic acid
≥96.0% (TLC)
Synonym(s):
N-(3α,7β-Dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oyl)glycine, N-[(3α,5β,7β)-3,7-Dihydroxy-24-oxocholan-24-yl]glycine, GUDCA, Glycylursodeoxycholic acid, Ursodeoxycholylglycine
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
synthetic
Quality Level
assay
≥96.0% (TLC)
form
powder
functional group
carboxylic acid
SMILES string
[H][C@@]12[C@]([C@](CC[C@@H](O)C3)(C)[C@]3([H])C[C@@H]2O)([H])CC[C@@]4(C)[C@@]1([H])CC[C@]4([H])[C@]([H])(C)CCC(NCC(O)=O)=O
InChI
1S/C26H43NO5/c1-15(4-7-22(30)27-14-23(31)32)18-5-6-19-24-20(9-11-26(18,19)3)25(2)10-8-17(28)12-16(25)13-21(24)29/h15-21,24,28-29H,4-14H2,1-3H3,(H,27,30)(H,31,32)/t15-,16+,17-,18-,19+,20+,21+,24+,25+,26-/m1/s1
InChI key
GHCZAUBVMUEKKP-XROMFQGDSA-N
Application
- Glycoursodeoxycholic Acid Alleviates Arterial Thrombosis via Suppressing Diacylglycerol Kinases Activity in Platelet.: Highlights the therapeutic potential of Glycoursodeoxycholic acid in alleviating arterial thrombosis by inhibiting diacylglycerol kinase activity in platelets (Yang et al., 2024).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Isobaric separation of bile acids and conjugates by LC-MS/MS on Ascentis® Express C18 column with excellent resolution and linearity.
Protocols
This method is particularly useful in research into the role of individual bile acids as signaling molecules; suitable for clinical laboratories to investigate potential mechanisms linked to gut hormone profiles and glycemic control.
Related Content
Bile Acids (BA) are synthesized in the liver and play important roles in cholesterol homeostasis, absorption of vitamins and lipids, and various key metabolic processes.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service