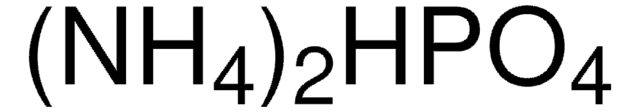30402
Ammonium phosphate dibasic
puriss. p.a., ACS reagent, reag. Ph. Eur., ≥98% (alkalimetric)
Synonym(s):
Ammonium hydrogenphosphate, Diammonium hydrogenphosphate, di-Ammonium hydrogenphosphate (sec)
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
ACS reagent
puriss. p.a.
Quality Level
agency
reag. Ph. Eur.
assay
≥98% (alkalimetric)
form
powder, crystals or granules
impurities
≤0.001% heavy metals (as Pb)
pH
7.7-8.1 (25 °C, 5%)
mp
155 °C (dec.) (lit.)
anion traces
chloride (Cl-): ≤0.001%
nitrate (NO3-): ≤0.003%
sulfate (SO42-): ≤0.01%
cation traces
Ca: ≤0.001%
Fe: ≤0.001%
K: ≤0.005%
Mg: ≤0.0005%
Na: ≤0.005%
storage temp.
room temp
SMILES string
N.N.OP(O)(O)=O
InChI
1S/2H3N.H3O4P/c;;1-5(2,3)4/h2*1H3;(H3,1,2,3,4)
InChI key
MNNHAPBLZZVQHP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
- Human Bone Paleoproteomics Utilizing the Single-Pot, Solid-Phase-Enhanced Sample Preparation Method to Maximize Detected Proteins and Reduce Humics.: This study demonstrates the application of ammonium phosphate dibasic in the preparation of human bone samples for paleoproteomics. The method enhances protein detection and reduces contamination, significantly improving the analysis of ancient proteins (Cleland, 2018).
- Effect of Mg(2+) doping on beta-alpha phase transition in tricalcium phosphate (TCP) bioceramics.: Ammonium phosphate dibasic is utilized in the synthesis of Mg-doped tricalcium phosphate bioceramics. The study investigates the phase transition behavior, which is critical for developing advanced biomaterials for medical applications (Frasnelli & Sglavo, 2016).
- Development and validation of a stability-indicating HPLC method for determination of voriconazole and its related substances.: The research outlines the use of ammonium phosphate dibasic in the development of a stability-indicating HPLC method for analyzing voriconazole. This method ensures accurate detection of the drug and its impurities, crucial for pharmaceutical quality control (Gu & Li, 2009).
- Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of the catalytic domain cellobiohydrolase I from Talaromyces emersonii.: Ammonium phosphate dibasic is employed in the crystallization process of cellobiohydrolase I. The study provides insights into the enzyme′s structure, aiding in the understanding of its catalytic mechanisms and potential industrial applications (Grassick et al., 2003).
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service