16201
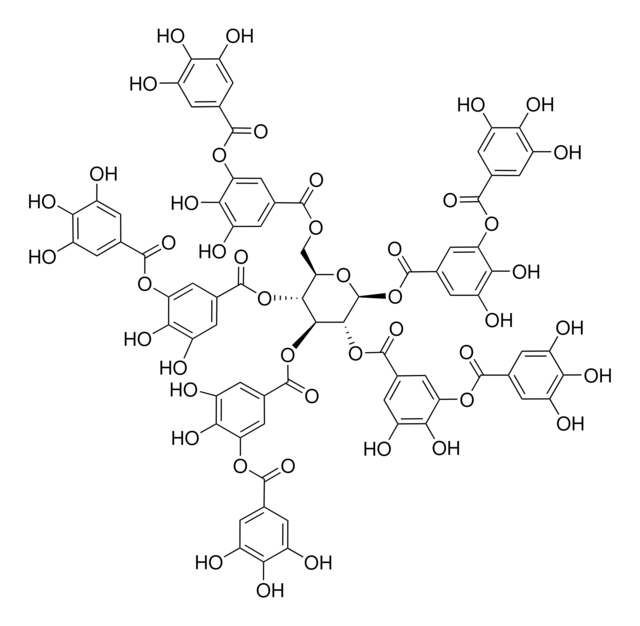
Tannic acid
puriss., meets analytical specification of USP, powder
Synonym(s):
Gallotannin, Tannin
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
puriss.
Quality Level
form
powder
autoignition temp.
980 °F
quality
meets analytical specification of USP
impurities
dextrines, gum matters, in accordance
resinous matters, in accordance
≤0.003% heavy metals (as Pb)
ign. residue
≤0.1% (as SO4)
loss
≤9% loss on drying, 105 °C, 2 h
mp
218 °C (lit.)
solubility
H2O: soluble 1 gm in 0.35ml
glycerol: soluble 1gm in 1 ml (warm)
acetone: very soluble
alcohol: freely soluble (Diluted)
alcohol: slightly soluble (Dehydrated)
alcohol: very soluble
benzene: insoluble
carbon disulfide: insoluble
carbon tetrachloride: insoluble
chloroform: insoluble
diethyl ether: insoluble
hexane: insoluble
petroleum ether: insoluble
cation traces
As: ≤3 mg/kg
application(s)
metabolomics
vitamins, nutraceuticals, and natural products
SMILES string
Oc1cc(cc(O)c1O)C(=O)Oc2cc(cc(O)c2O)C(=O)OC[C@H]3O[C@@H](OC(=O)c4cc(O)c(O)c(OC(=O)c5cc(O)c(O)c(O)c5)c4)[C@H](OC(=O)c6cc(O)c(O)c(OC(=O)c7cc(O)c(O)c(O)c7)c6)[C@@H](OC(=O)c8cc(O)c(O)c(OC(=O)c9cc(O)c(O)c(O)c9)c8)[C@@H]3OC(=O)c%10cc(O)c(O)c(OC(=O)c%11cc(O)c(O)c(O)c%11)c%10
InChI
1S/C76H52O46/c77-32-1-22(2-33(78)53(32)92)67(103)113-47-16-27(11-42(87)58(47)97)66(102)112-21-52-63(119-72(108)28-12-43(88)59(98)48(17-28)114-68(104)23-3-34(79)54(93)35(80)4-23)64(120-73(109)29-13-44(89)60(99)49(18-29)115-69(105)24-5-36(81)55(94)37(82)6-24)65(121-74(110)30-14-45(90)61(100)50(19-30)116-70(106)25-7-38(83)56(95)39(84)8-25)76(118-52)122-75(111)31-15-46(91)62(101)51(20-31)117-71(107)26-9-40(85)57(96)41(86)10-26/h1-20,52,63-65,76-101H,21H2/t52-,63-,64+,65-,76+/m1/s1
InChI key
LRBQNJMCXXYXIU-PPKXGCFTSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
- as a reference standard to measure the total hydrolyzable tannins in Oak root bark tannin-methanol extract using a UV/Vis spectrophotometer
- as a blood-brain barrier (BBB) impermeable, transcytosis-inhibiting drug in spheroid culture medium
- as a flushing agent to test its effects on metal ions, total organic carbon, and organic matter of soil
- as an inhibitor of free ovalbumin (OVA) uptake by the endocytic mechanism on dendritic cells
Biochem/physiol Actions
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 2
flash_point_f
390.2 °F
flash_point_c
199 °C
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service