901725
1-(Tert-butyl) 2-methyl (2S,4R)-4-((4-bromo-7-fluoroisoindoline-2-carbonyl)oxy)pyrrolidine-1,2-dicarboxylate
Synonym(s):
Aryl halide chemistry informer library compound X4
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C20H24BrFN2O6
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
487.32
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352101
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
form
powder or crystals
mp
157.61 °C
Application
This product is Informer compound X4 of the Aryl halide chemistry informer library developed by chemists at Merck & Co. Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, U.S., which contains 18 drug-like molecules representative of those encountered in complex synthesis. By screening a new reaction against the informer library, chemists can directly compare and analyse a reaction′s successes and shortcomings among different methods and various research teams. It may also be used to facilitate deeper method development for performance or utility.
Caution
Not fully tested
Related product
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Thomas J Greshock et al.
Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English), 55(44), 13714-13718 (2016-10-22)
The reactivity of a representative set of 17 organozinc pivalates with 18 polyfunctional druglike electrophiles (informers) in Negishi cross-coupling reactions was evaluated by high-throughput experimentation protocols. The high-fidelity scaleup of successful reactions in parallel enabled the isolation of sufficient material
Peter S Kutchukian et al.
Chemical science, 7(4), 2604-2613 (2016-04-21)
Major new advances in synthetic chemistry methods are typically reported using simple, non-standardized reaction substrates, and reaction failures are rarely documented. This makes the evaluation and choice of a synthetic method difficult. We report a standardized complex molecule diagnostic approach
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service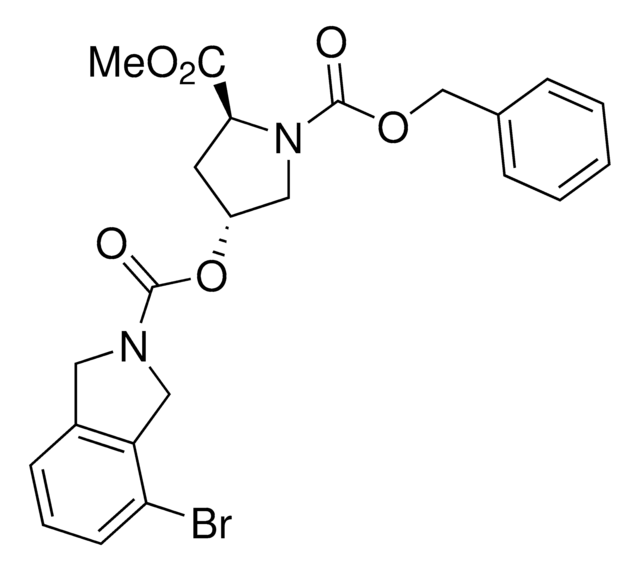
![(R)-2-(5-Bromo-4-(4-chlorobenzyl)-7-fluoro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrocyclopenta[b]indol-3-yl)acetic acid](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/321/793/9c59bf88-c483-4a85-a559-53ba29e916d1/640/9c59bf88-c483-4a85-a559-53ba29e916d1.png)
![(S)-6-Chloro-4-(cyclopropylethynyl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazin-2-one](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/243/541/d5c488f9-cd03-4bf8-8fe0-56dd8f960d6f/640/d5c488f9-cd03-4bf8-8fe0-56dd8f960d6f.png)
![tert-Butyl (R)-3-(2-acetamidopropan-2-yl)-6-chloro-5-methyl-2,3-dihydrospiro[indene-1,4′-piperidine]-1′-carboxylate](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/719/283/e2c466e0-b4df-4961-9844-bfffbe187f3e/640/e2c466e0-b4df-4961-9844-bfffbe187f3e.png)
![N-(tert-Butyl)-4′-((6-iodo-4-oxo-2-propylquinazolin-3(4H)-yl)methyl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-sulfonamide](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/223/993/31506e33-20ed-40d4-930b-6a854b25190c/640/31506e33-20ed-40d4-930b-6a854b25190c.png)
![Methyl 2-(9-bromo-2,3-dioxo-2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-1H,5H-pyrido[1,2,3-de]quinoxalin-5-yl)acetate ≥90%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/955/217/e6cb560d-1177-4dc4-b686-7c790e13f1f4/640/e6cb560d-1177-4dc4-b686-7c790e13f1f4.png)