725684
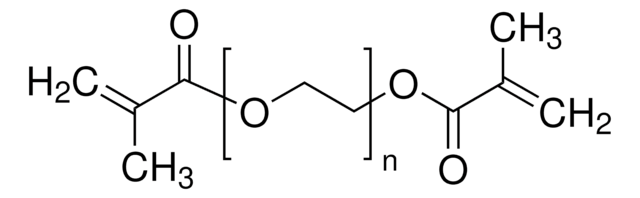
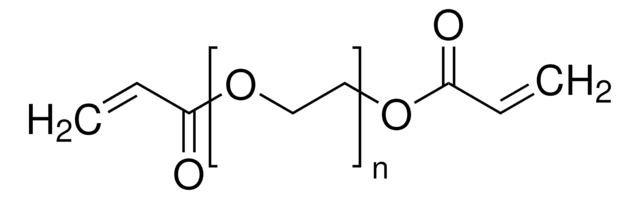
Poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate
average MN 10,000, cross-linking reagent polymerization reactions, methacrylate, ≤1, 500 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor (may contain)
Synonym(s):
Polyethylene glycol, PEG dimethacrylate
About This Item
Recommended Products
product name
Poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate, average Mn 10,000, contains MEHQ as inhibitor
form
powder
mol wt
average Mn 10,000
contains
MEHQ as inhibitor
≤1,500 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor (may contain)
reaction suitability
reagent type: cross-linking reagent
reaction type: Polymerization Reactions
bp
>200 °C/2 mmHg (lit.)
transition temp
Tm 56-61 °C
Mw/Mn
≤1.1
Ω-end
methacrylate
α-end
methacrylate
polymer architecture
shape: linear
functionality: homobifunctional
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
OCCO.CC(=C)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C10H14O4/c1-7(2)9(11)13-5-6-14-10(12)8(3)4/h1,3,5-6H2,2,4H3
InChI key
STVZJERGLQHEKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Preparation Note
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
In this article, we will discuss the benefits and limitations of several 2D and 3D scaffold patterning techniques that can be applied in the presence of cells. Although these methods will be discussed in the context of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)-based hydrogels, they can technically be applied to any optically transparent, photoactive substrate.
The use of hydrogel-based biomaterials for the delivery and recruitment of cells to promote tissue regeneration in the body is of growing interest. This article discussed the application of hydrogels in cell delivery and tissue regeneration.
In the past two decades, tissue engineering and regenerative medicine have become important interdisciplinary fields that span biology, chemistry, engineering, and medicine.
Progress in biotechnology fields such as tissue engineering and drug delivery is accompanied by an increasing demand for diverse functional biomaterials. One class of biomaterials that has been the subject of intense research interest is hydrogels, because they closely mimic the natural environment of cells, both chemically and physically and therefore can be used as support to grow cells. This article specifically discusses poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels, which are good for biological applications because they do not generally elicit an immune response. PEGs offer a readily available, easy to modify polymer for widespread use in hydrogel fabrication, including 2D and 3D scaffold for tissue culture. The degradable linkages also enable a variety of applications for release of therapeutic agents.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service