All Photos(3)
About This Item
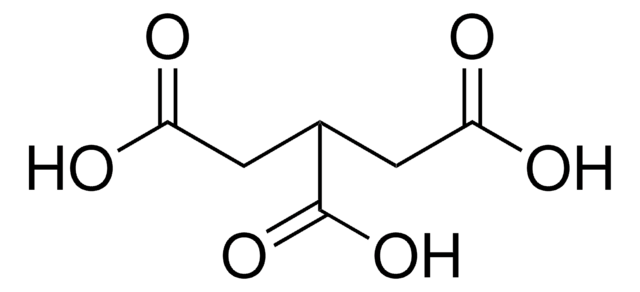
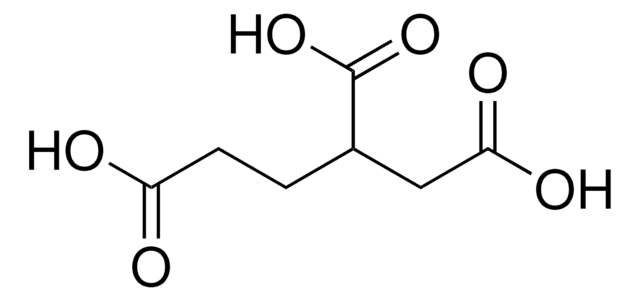
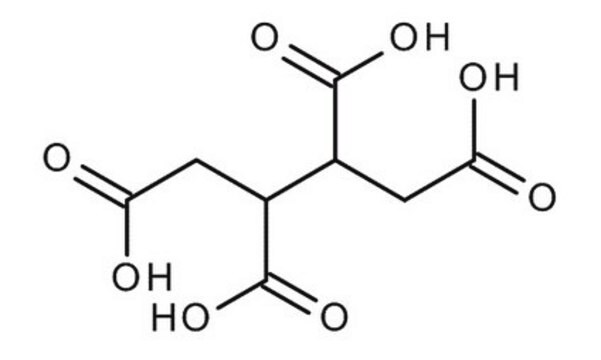
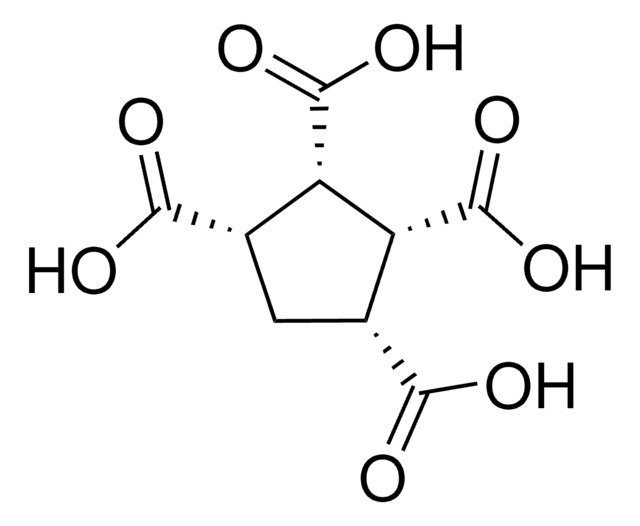
Linear Formula:
[-CH(CO2H)CH2CO2H]2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
234.16
Beilstein/REAXYS Number:
1729167
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12162002
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
Quality Level
assay
99%
form
powder
mp
195-197 °C (dec.) (lit.)
SMILES string
OC(=O)CC(C(CC(O)=O)C(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C8H10O8/c9-5(10)1-3(7(13)14)4(8(15)16)2-6(11)12/h3-4H,1-2H2,(H,9,10)(H,11,12)(H,13,14)(H,15,16)
InChI key
GGAUUQHSCNMCAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
1,2,3,4-Butanetetracarboxylic acid (BTCA) is utilized as a cross-linking agent and as a building block for the synthesis of specialized polymers for the formulation of resins, polymers, coatings, and adhesives.
Application
1,2,3,4-Butanetetracarboxylic acid (BTCA) can be used as a cross-linking agent:
- To functionalize cotton fabric. BTCA-treated fabric shows improved anti-pilling, wrinkle resistance, and fire-retardant properties.
- To fabricate flexible, free-standing nanocellulose membranes. The cross-linking with BTCA improves water stability and ionic conductivity of membranes.
signalword
Warning
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Mattia Alberto Lucchini et al.
ACS applied materials & interfaces, 10(35), 29599-29607 (2018-08-08)
In this work, we report a versatile approach for the development of an in-flow purification water system under solar illumination. Cellulose nanofibrils (CNFs) were impregnated with TiO2 nanoparticles using water as a solvent to obtain hybrid CNF/TiO2 monoliths with 98%
Limin Guo et al.
Carbohydrate polymers, 179, 333-340 (2017-11-08)
Cellulose nanofibril (CNF) aerogel is highly flammable and its mechanical strength is very soft, which is unfavourable due to safety concerns and impractical when used as the thermal insulation material. In this work, we used N-methylol dimethylphosphonopropionamide (MDPA) and 1,2,3,4-butanetetracarboxylic
Solmaz Heydarifard et al.
Carbohydrate polymers, 181, 1086-1092 (2017-12-20)
Development of a foam-formed cellulose filter paper with high wet strength was carried out for application as a drinking water filter. The wet strength and antimicrobial activity of cellulose foam paper against several bacteria species (Bacillus subtilis MTCC 441 (Gram
Asli Celebioglu et al.
Scientific reports, 7(1), 7369-7369 (2017-08-09)
Water pollution is a serious concern for public health and environment in today's world; hence, there exists a strong demand to develop cost-effective, sustainable and eco-friendly membranes. Here, we produce a highly efficient molecular filter membrane based on bio-renewable material;
Peipei Wang et al.
Carbohydrate polymers, 218, 103-111 (2019-06-22)
Environmentally friendly, sustainable, and high-performance thermal insulators are in high demand. Petroleum-based insulator foams usually have high thermal conductivity and pose health hazards. Here, we report ultralight composite foams that are highly strong, elastic, and super-insulating. The foams are composed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service