CS1030
Chitinase Assay Kit, Fluorimetric
sufficient for 200 multiwell tests
Synonim(y):
Zestaw do wykrywania chitynazy
Zaloguj sięWyświetlanie cen organizacyjnych i kontraktowych
About This Item
Kod UNSPSC:
12161503
NACRES:
NA.84
Polecane produkty
zastosowanie
sufficient for 200 multiwell tests
Poziom jakości
Warunki transportu
wet ice
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
informacje o genach
human ... CHIT1(1118)
Opis ogólny
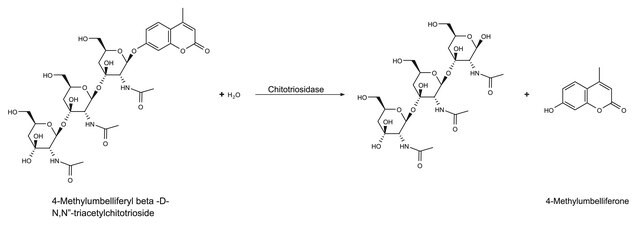
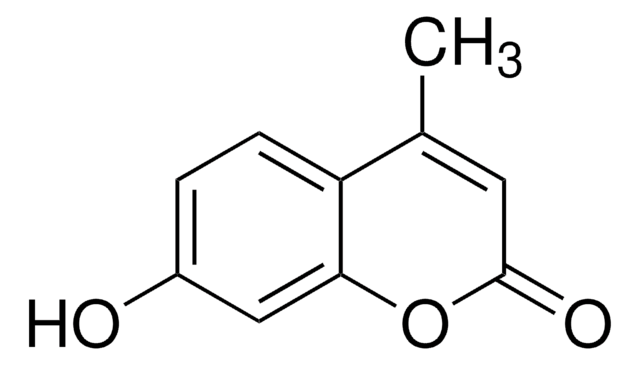
The kit assay is based on the enzymatic hydrolysis of chitinase substrates. This enzymatic hydrolysis releases 4-methylumbelliferone (4MU), which upon ionization in basic pH, can be measured fluorimetrically at an excitation wavelength of 360 nm and an emission wavelength of 450 nm. The use of fluorimetric substrates provides a very sensitive detection system.
Zastosowanie
The Chitinase Assay Kit provides all the reagents required for efficient and sensitive detection of chitinase activity in fungal and bacterial growth media, macrophage lysates, and purified enzyme preparations. In addition, the kit provides three different substrates for the detection of the various types of the chitinolytic activity:
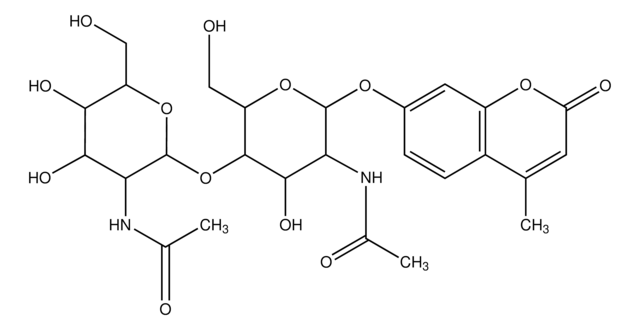
- 4-Methylumbelliferyl N,N′-diacetyl-β-D-chitobioside - substrate suitable for exochitinase activity detection (chitobiosidase activity)
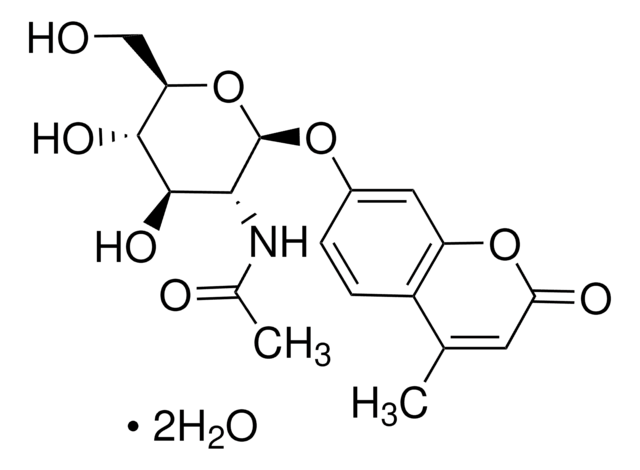
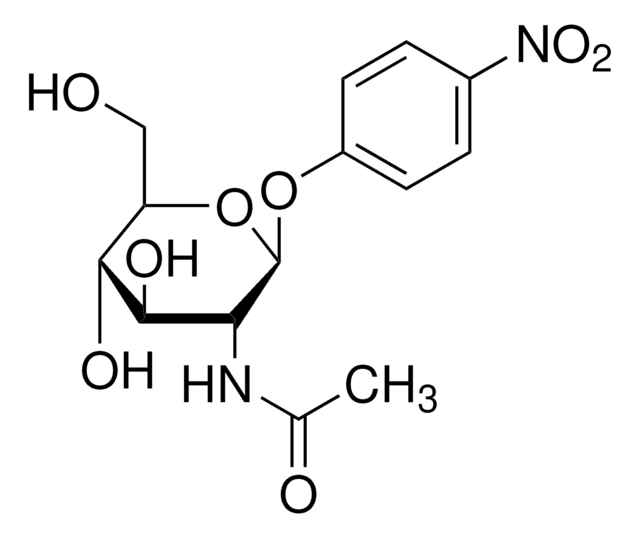
- 4-Methylumbelliferyl N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminide - substrate suitable for exochitinase activity detection (β-N-acetylglucosaminidase activity)
- 4-Methylumbelliferyl β-D-N,N′,N′′-triacetylchitotriose - substrate suitable for endochitinase activity detection
Działania biochem./fizjol.
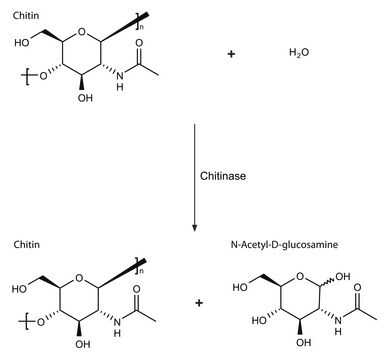
Chitinase catalyzes the hydrolytic cleavage of the β-1→4-glycoside bond present in biopolymers of N-acetylglucosamine, primarily in chitin. Chitinases are widely distributed in living organisms and are found in fungi, bacteria, parasites, plants, and animals. They are classified in families based on amino acid sequence similarities.
The chitinolytic enzymes are also categorized based on their enzymatic action on chitin substrates. Endochitinases are defined as the enzymes catalyzing the random cleavage at internal points in the chitin chain. Exochitinases catalyze the progressive release of acetylchitobiose or N-acetylglucosamine from the non-reducing end of chitin, and are referred to as chitobiosidase and β-N-acetylglucosaminidase, respectively.
Chitinases perform different functions in different organisms. In bacteria, they are mainly involved in nutritional processes. In yeast and various fungi, these enzymes participate in morphogenesis. In animals and plants, chitinases primarily play a role in the defense of the organism against pathogen attack.
The chitinolytic enzymes are also categorized based on their enzymatic action on chitin substrates. Endochitinases are defined as the enzymes catalyzing the random cleavage at internal points in the chitin chain. Exochitinases catalyze the progressive release of acetylchitobiose or N-acetylglucosamine from the non-reducing end of chitin, and are referred to as chitobiosidase and β-N-acetylglucosaminidase, respectively.
Chitinases perform different functions in different organisms. In bacteria, they are mainly involved in nutritional processes. In yeast and various fungi, these enzymes participate in morphogenesis. In animals and plants, chitinases primarily play a role in the defense of the organism against pathogen attack.
Przydatność
The kit was tested and found suitable for Trichoderma viride and Streptomyces griseus, along with Hela, Jurkat, CHO, NIH-3T3, U-837 mammalian cell lines, human macropages, rat lung, kidney, liver, and brain tissue.
Uwaga dotycząca przygotowania
Use ultrapure water for preparation of reagents.
Ta strona może zawierać tekst przetłumaczony maszynowo.
Tylko elementy zestawu
Numer produktu
Opis
- Assay Buffer 25 mL
- 4-Methylumbelliferyl N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminide 5 mg
- 4-Methylumbelliferyl β-D-N,N′-diacetylchitobioside hydrate 5 mg
- 4-Methylumbelliferyl β-D-N,N′,N′′-triacetylchitotriose 5 mg
- Chitinase from Trichoderma viride 1 mg
- 4-Methylumbelliferone Standard Solution, 50 mg/mL 1 mL
- Sodium Carbonate 2 g
- Dimethyl Sulfoxide 1 mL
Zobacz wszystko (8)
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Eye Irrit. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1
Kod klasy składowania
10 - Combustible liquids
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Zhangfa Song et al.
BMC cancer, 19(1), 629-629 (2019-06-27)
This study aimed to evaluate the value of chitinase activity in prognosticating the occurrence of metastasis in and prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer (CRC). The chitinase activity in four different groups, namely 335 CRC patients without distant metastasis at
Ying-ying Lu et al.
Journal of Zhejiang University. Science. B, 15(6), 566-574 (2014-06-07)
Aging is one of the contributing risk factors for kidney diseases. Accumulating evidence prompts the view that telomere length in kidney tissue cells is an indicator for organismal aging. Previously identified aging markers (cathelin-related antimicrobial peptide (CRAMP), stathmin, elongation factor-1α
Jéssica Rodrigues et al.
Scientific reports, 5, 11717-11717 (2015-07-15)
Cryptococcus gattii is one of the causative agents of human cryptococcosis. Highly virulent strains of serotype B C. gattii have been studied in detail, but little information is available on the pathogenic properties of serotype C isolates. In this study
Haoran Ma et al.
Journal of experimental botany, 67(19), 5799-5809 (2016-09-25)
Two unlinked semi-dominant loci, A (NIC1) and B (NIC2), control nicotine and related alkaloid biosynthesis in Burley tobaccos. Mutations in either or both loci (nic1 and nic2) lead to low nicotine phenotypes with altered environmental stress responses. Here we show
Svetlana E Belova et al.
Frontiers in microbiology, 9, 2775-2775 (2018-12-05)
Members of the Acidobacteria are among the most efficient colonizers of acidic terrestrial habitats but the key traits underlying their environmental fitness remain to be understood. We analyzed indigenous assemblages of Acidobacteria in a lichen-covered acidic (pH 4.1) soil of
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej