Opis ogólny
Sialoadhesin (UniProt Q9BZZ2; also known as CD169, Sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin 1, Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin 1, Siglec-1) is encoded by the SIGLEC1 (also known as SN) gene (Gene ID 6614) in human. Sialoadhesin/CD169/Siglec-1 is the founding member of the sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin lectins (Siglec) expressed on a variety of leukocytes and stromal cells. Sialoadhesin is initially produced with a signal sequence (a.a. 1-19), the removal of which yields the mature protein with a large extracellular portion (a.a. 20-1641), followed by a transmembrane segment (a.a. 1642-1662), and a short cytoplasmic tail (a.a. 1663-1709) with no known signal transduction or endocytosis motifs. The extracellular portion contains an N-terminal Ig-like V-type domain (a.a. 20-136), followed by sixteen Ig-like C2-type domains. Sialoadhesin is highly expressed on the subcapsular sinus (SCS) and medullary macrophages in lymph node (LN) and on marginal metallophilic macrophages in the marginal zone (MZ) of spleen. Although sialic acids are found on the surface of all cells and most secreted proteins, Only heavily sialylated, multimeric structures are captured by Sialoadhesin on macrophages via its N-terminal Ig-like V-type domain due to a low (millimolar) affinity toward sialylic acid. Sialoadhesin-mediated sialic-acid recognition allows macrophages to engage sialylated pathogens and stimulate inflammatory responses. Sialoadhesin is also reported to capture of B cell-derived exosomes via their surface-expressed α2, 3-linked sialic acids. In the lymph node, exosomes are not retained in the subcapsular sinus of Siglec1-knockout mice and penetrate deeper into the paracortex, causing an enhanced response to antigen-pulsed exosomes among Siglec1-/- mice.
Specyficzność
Expected to react with all three spliced isoforms of human Siglec-1 (CD169)/Sialoadhesin reported by UniProt (Q9BZZ2).
Immunogen
Epitope: Ig-like V-type domain
GST-tagged recombinant human Siglec-1 (CD169) N-terminal fragment containing the Ig-like V-type domain.
Zastosowanie
Anti-Siglec-1 (CD169) Antibody, clone 5F1.1 is an antibody against Siglec-1 for use in Western Blotting, Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin).
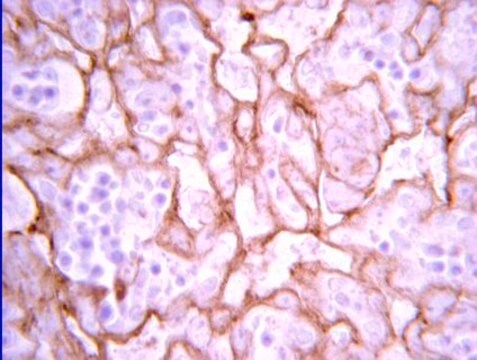
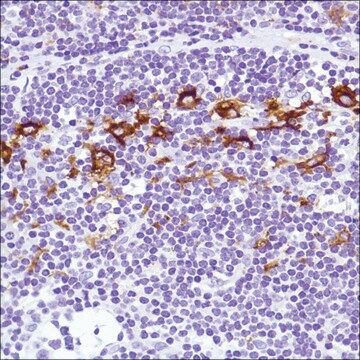
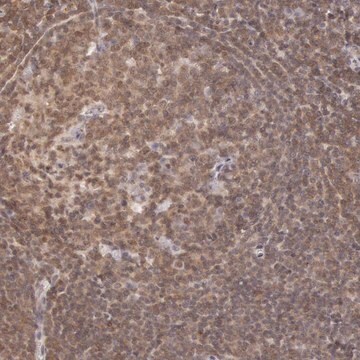
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A 1:50 dilution from a representative lot detected Siglec-1 (CD169) in human spleen, human tonsil, and mouse spleen tissue.
Research Category
Cell Structure
Research Sub Category
ECM Proteins
Jakość
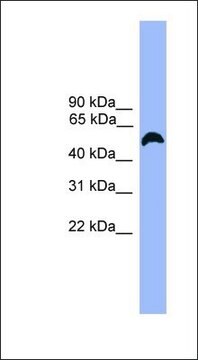
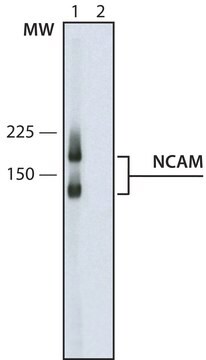
Evaluated by Western Blotting in human lymph node tissue lysate.
Western Blotting Analysis: 0.5 µg/mL of this antibody detected Siglec-1 (CD169) in 10 µg of human lymph node tissue lysate.
Opis wartości docelowych
~200 kDa observed. Target band size appears larger than the calculated molecular weights of 182.6 kDa (isoform 1), 175.7 kDa (isoform 2), and 181.7 kDa (isoform 3) due to glycosylation.
Postać fizyczna
Format: Purified
Protein G Purified
Purified mouse monoclonal IgG2aκ antibody in buffer containing 0.1 M Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl with 0.05% sodium azide.
Przechowywanie i stabilność
Stable for 1 year at 2-8°C from date of receipt.
Inne uwagi
Concentration: Please refer to lot specific datasheet.
Oświadczenie o zrzeczeniu się odpowiedzialności
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
This page may contain text that has been machine translated.