MAB5204
Anti-Agrin Antibody
Chemicon®, from mouse
Synonim(y):
Anti-AGRIN, Anti-CMSPPD
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
mouse
Poziom jakości
forma przeciwciała
purified immunoglobulin
rodzaj przeciwciała
primary antibodies
klon
monoclonal
reaktywność gatunkowa
mouse, rat
producent / nazwa handlowa
Chemicon®
metody
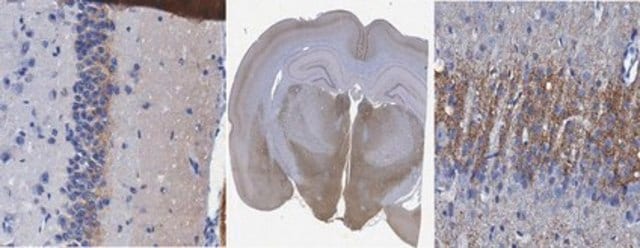
immunocytochemistry: suitable
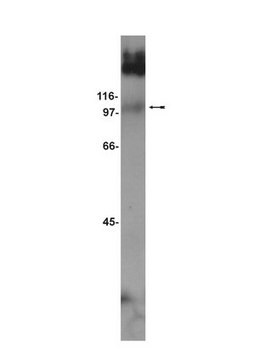
western blot: suitable
izotyp
IgG1
numer dostępu NCBI
numer dostępu UniProt
Warunki transportu
dry ice
docelowa modyfikacja potranslacyjna
unmodified
informacje o genach
human ... AGRN(375790)
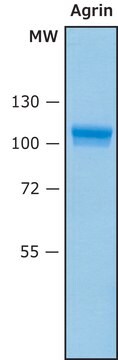
Specyficzność
Immunogen
Zastosowanie
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by the end user.
Neuroscience
Growth Cones & Axon Guidance
Synapse & Synaptic Biology
Postać fizyczna
Przechowywanie i stabilność
Inne uwagi
Informacje prawne
Oświadczenie o zrzeczeniu się odpowiedzialności
Nie możesz znaleźć właściwego produktu?
Wypróbuj nasz Narzędzie selektora produktów.
Kod klasy składowania
10 - Combustible liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 2
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej