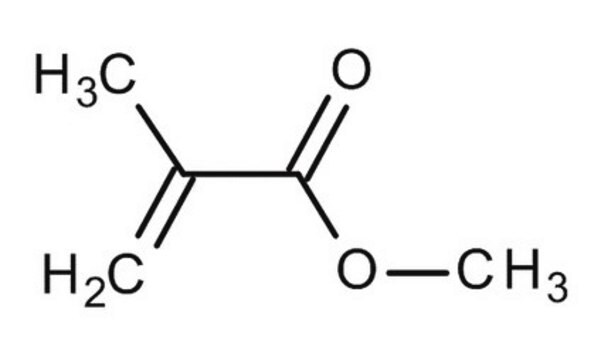
Key Documents
M55909
Methyl methacrylate
contains ≤30 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor, 99%
Synonim(y):
Methacrylic acid methyl ester, Methyl 2-methylprop-2-enoate, Methyl 2-methylpropenoate
About This Item
Polecane produkty
gęstość pary
3.5 (vs air)
Poziom jakości
ciśnienie pary
29 mmHg ( 20 °C)
Próba
99%
temp. samozapłonu
815 °F
zawiera
≤30 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor
granice wybuchowości
12.5 %
współczynnik refrakcji
n20/D 1.414 (lit.)
tw
100 °C (lit.)
mp
−48 °C (lit.)
gęstość
0.936 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
temp. przechowywania
2-8°C
ciąg SMILES
COC(=O)C(C)=C
InChI
1S/C5H8O2/c1-4(2)5(6)7-3/h1H2,2-3H3
Klucz InChI
VVQNEPGJFQJSBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
- Lanthanide-complex grafted poly(methyl methacrylate-co-maleic anhydride) copolymer. These luminescent polymers exhibit high thermal stability and can be used as luminous layers for optoelectronic devices.
- Poly (methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), is a common material used in the production of lenses for concentrating photovoltaic (CPV) modules.
- Polymethyl methacrylate, methyl methacrylate crosspolymer, and methyl methacrylate/glycol dimethacrylate crosspolymers. These polymers are used in cosmetic surgery, dentistry, and joint replacement.
- Poly (methyl methacrylate) (PMMA)-based personalized medical devices.
- Interpenetrating methyl methacrylate-based polymeric networks with enhanced thermal and mechanical properties.
- Poly(methyl methacrylate-co-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (PMMA-co-PHEMA) copolymers by emulsion copolymerization. These copolymers form thermooxidatively stable and ductile films.
- Poly(methyl methacrylate) nanoparticles through differential microemulsion polymerization.
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Flam. Liq. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1B - STOT SE 3
Organy docelowe
Respiratory system
Kod klasy składowania
3 - Flammable liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 1
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
50.0 °F - closed cup
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
10 °C - closed cup
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
RAFT (Reversible Addition Fragmentation chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
The manufacture of monomers for use in ophthalmic applications is driven by the need for higher purity, improved reliability of manufacturing supply, but ultimately by the need for the increased comfort, convenience, and safety of contact lens wearers. Daily wear contact lenses have the potential to fill this need for many customers; however, their widespread use is constrained by higher costs compared to weekly- or monthly-based lenses. New approaches that improve cost structure and result in higher quality raw materials are needed to help make contact lenses more affordable and accelerate growth of the contact lens market.
Protokoły
We presents an article about ARGET ATRP, and its procedure for PMMA polymer brush growth. Surface preparation before polymer brush growth consists of two steps: surface cleaning and initiator monolayer deposition.
Sfery polimerowe służą jako szablony kryształów. Metody syntezy dają duże ilości.
Monodisperse, surfactant-free polymer spheres for use as colloidal crystal templates can be easily obtained in reasonably large quantities. Typical synthesis methods for poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) and poly(styrene) (PS) by emulsifier free emulsion polymerization are described below and yield spheres several hundred nanometers in diameter.
RAFT (Reversible Addition-Fragmentation chain Transfer) is a form of living radical polymerization involving conventional free radical polymerization of a substituted monomer in the presence of a suitable chain transfer (RAFT) reagent.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej