Kluczowe dokumenty
764698
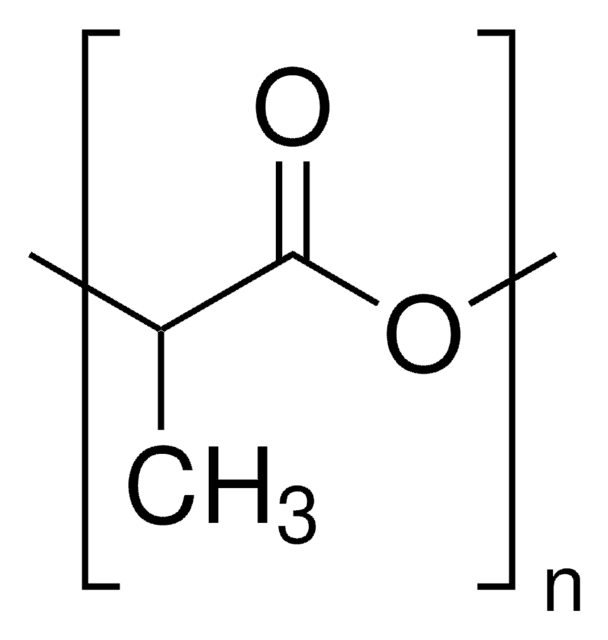
Poly(L-lactide)
average Mn 20,000, PDI ≤1.1
Synonim(y):
PLA, PLLA, Polylactide, L-Lactide polymer, PLA, Poly(L-Lactic acid)
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Formularz
solid
Poziom jakości
aktywność optyczna
[α]22/D -153°, c = 0.5% in chloroform
masa cząsteczkowa
average Mn 20,000
ramy czasowe degradacji
>3 years
temp. przejścia
Tm 167-172 °C
PDI
≤1.1
temp. przechowywania
2-8°C
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
Cechy i korzyści
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
Professor Aran (Claremont University, USA) thoroughly discusses the engineering of graphene based materials through careful functionalization of graphene oxide, a solution processable form of graphene.
Local delivery of bioactive molecules using an implantable device can decrease the amount of drug dose required as well as non-target site toxicities compared to oral or systemic drug administration.
Syntetyczne poliestry alifatyczne dominują wśród biomateriałów resorbowalnych w zastosowaniach klinicznych.
The world of commercial biomaterials has stagnated over the past 30 years as few materials have successfully transitioned from the bench to clinical use. Synthetic aliphatic polyesters have continued to dominate the field of resorbable biomaterials due to their long history and track record of approval with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej