추천 제품
일반 설명
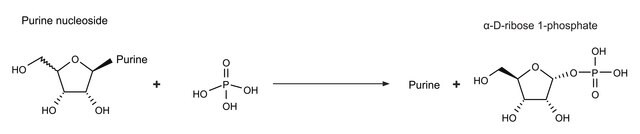
Polynuclotide phosphorlyase in spinach chloroplasts acts as a exonuclease and a poly(A) polymerase.
애플리케이션
Polynucleotide phosphorylase has been used in a study to discover that a major function of PNPase is the synthesis of CDP. It has also been used in a study to investigate the enzyme responsible for RNA 3′-tail synthesis in S. coelicolor.
생화학적/생리학적 작용
Polynucleotide phosphorylase (PNPase) is a bifunctional enzyme with a phosphorolytic 3′ to 5′ exoribonuclease activity and a 3′-terminal oligonucleotide polymerase activity.
Polynucleotide phosphorylase localizes to the intermembrane space of mitochondria and has a critical function in regulating mitochondrial homeostasis in human cells.
단위 정의
One unit will polymerize 1.0 μmole of ADP, releasing 1.0 μmole of inorganic phosphate in 15 minutes, at pH 9.1 at 37 °C.
Supplied as a solution in 20 mM Hepes buffer pH 7.9, 0.1 mM EDTA, 2 mM DTT, 12.5 mM MgCl2, 60 mM KCl, 20% (w/v) Glycerol
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
이미 열람한 고객
Patricia Bralley et al.
Microbiology (Reading, England), 152(Pt 3), 627-636 (2006-03-04)
As in other bacteria, 3'-tails are added post-transcriptionally to Streptomyces coelicolor RNA. These tails are heteropolymeric, and although there are several candidates, the enzyme responsible for their synthesis has not been definitively identified. This paper reports on three candidates for
Ruth Rott et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 278(18), 15771-15777 (2003-02-26)
The mechanism of RNA degradation in Escherichia coli involves endonucleolytic cleavage, polyadenylation of the cleavage product by poly(A) polymerase, and exonucleolytic degradation by the exoribonucleases, polynucleotide phosphorylase (PNPase) and RNase II. The poly(A) tails are homogenous, containing only adenosines in
A Danchin
DNA research : an international journal for rapid publication of reports on genes and genomes, 4(1), 9-18 (1997-02-28)
Genome comparison permits identification of chromosome regions conserved during evolution. Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli are so distant that there exists very few conserved landmarks in their genome organisation. Analysis of the conserved cmk rpsA cluster pinpointed the importance of
G G Liou et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98(1), 63-68 (2001-01-03)
RNase E isolated from Escherichia coli is contained in a multicomponent "degradosome" complex with other proteins implicated in RNA decay. Earlier work has shown that the C-terminal region of RNase E is a scaffold for the binding of degradosome components
Peter Lengyel
Annual review of microbiology, 66, 27-38 (2012-09-22)
2011 marked the fiftieth anniversary of breaking the genetic code in 1961. Marshall Nirenberg, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) scientist who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1968 for his role in deciphering the code
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.