추천 제품
일반 설명
The monoclonal Anti-FLAG BioM2 mouse antibody is covalently attached to biotin by hydrazide linkage. The antibody recognizes the FLAG sequence at the N-terminus, Met-N-terminus or C-terminus of FLAG fusion porteins.
애플리케이션
Biotin-labeled antibody is used for immunodetection methods using avidin- or streptavidin-conjugated reporter enzymes such as streptavidin-peroxidase. Primary antibody conjugates are preferred when using murine cells as the recombinant protein host.
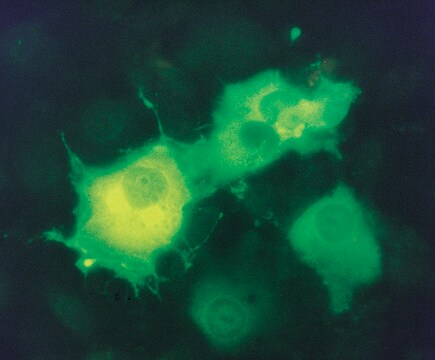
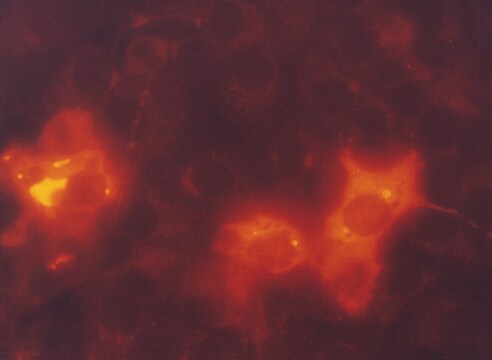
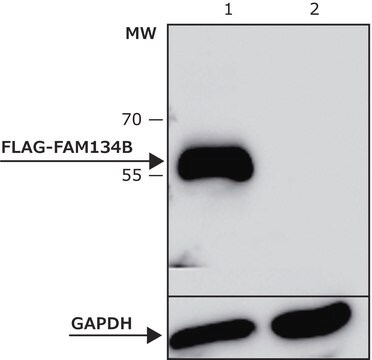
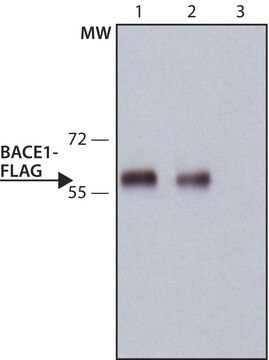
Antibody is suitable for immunofluorescence, western blotting, microscopy applications and for the formation of avidin-biotin complexes.
Learn more product details in our FLAG® application portal.
Antibody is suitable for immunofluorescence, western blotting, microscopy applications and for the formation of avidin-biotin complexes.
Learn more product details in our FLAG® application portal.
물리적 형태
Solution in 50% glycerol, 10 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.25, containing 150 mM NaCl and 0.02% sodium azide
제조 메모
Dilute antibody in TBS (.05M Tris, pH7.4, with .15M NaCl) to a final concentration of 1-10μg/mL.
법적 정보
ANTI-FLAG is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
FLAG is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
적합한 제품을 찾을 수 없으신가요?
당사의 제품 선택기 도구.을(를) 시도해 보세요.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
이미 열람한 고객
Hong-Won Lee et al.
Nature communications, 4, 1505-1505 (2013-02-21)
Co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) has become a standard technique, but its protein-band output provides only static, qualitative information about protein-protein interactions. Here we demonstrate a real-time single-molecule co-IP technique that generates real-time videos of individual protein-protein interactions as they occur in unpurified
Yoori Kim et al.
Scientific reports, 7(1), 2071-2071 (2017-05-20)
Single-molecule studies of protein-nucleic acid interactions frequently require site-specific modification of long DNA substrates. The bacteriophage λ is a convenient source of high quality long (48.5 kb) DNA. However, introducing specific sequences, tertiary structures, and chemical modifications into λ-DNA remains technically
Helen Hwang et al.
Scientific reports, 4, 6391-6391 (2014-09-30)
The ends of eukaryotic chromosomes are capped by telomeres which consist of tandem G-rich DNA repeats stabilized by the shelterin protein complex. Telomeres shorten progressively in most normal cells due to the end replication problem. In more than 85% of
Qing Xu et al.
Nature communications, 8(1), 425-425 (2017-09-06)
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) has a critical role in diverse cellular events including inflammation, apoptosis and necroptosis through different signaling complexes. However, little is known about how the transition from inflammatory signaling to the engagement of death pathways is modulated.
Kenichiro Kawai et al.
PloS one, 6(11), e27106-e27106 (2011-11-11)
Nanoparticles (NPs) are small entities that consist of a hydroxyapatite core, which can bind ions, proteins, and other organic molecules from the surrounding environment. These small conglomerations can influence environmental calcium levels and have the potential to modulate calcium homeostasis
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.