추천 제품
Grade
certified reference material
Agency
BCR®
제조업체/상표
JRC
기술
HPLC: suitable
gas chromatography (GC): suitable
bp
304 °C (lit.)
mp
53-57 °C (lit.)
density
1.223 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
형식
neat
저장 온도
2-8°C
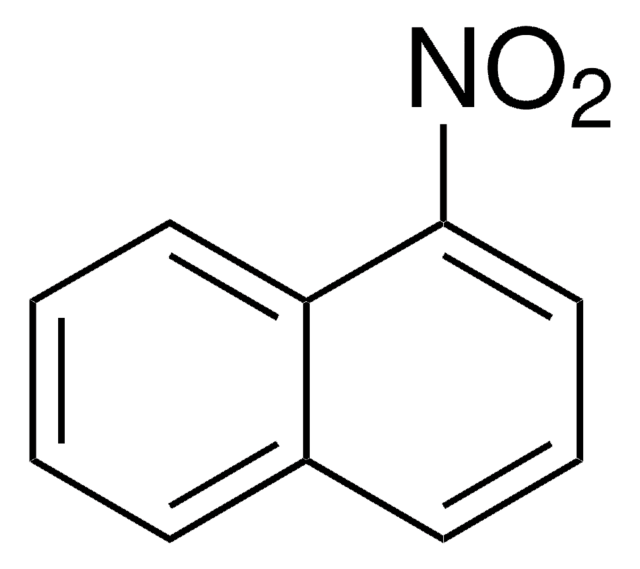
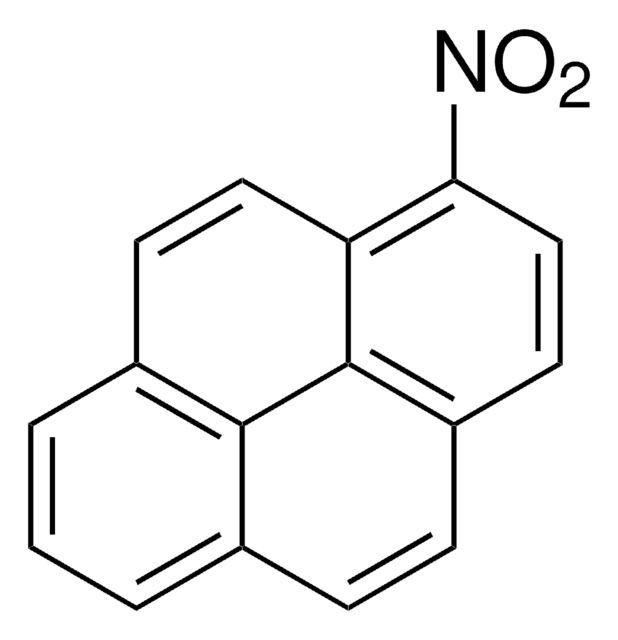
SMILES string
[O-][N+](=O)c1cccc2ccccc12
InChI
1S/C10H7NO2/c12-11(13)10-7-3-5-8-4-1-2-6-9(8)10/h1-7H
InChI key
RJKGJBPXVHTNJL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
유사한 제품을 찾으십니까? 방문 제품 비교 안내
일반 설명
1-Nitronaphthalene, belonging to the class of nitrated-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, is persistent in the environment. It is produced from direct sources such as diesel, gasoline exhaust and gas-phase reactions of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) with oxides of nitrogen.
분석 메모
For more information please see:
BCR306
BCR306
법적 정보
BCR is a registered trademark of European Commission
신호어
Warning
유해 및 위험 성명서
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Flam. Sol. 2
Storage Class Code
4.1B - Flammable solid hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
개인 보호 장비
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
가장 최신 버전 중 하나를 선택하세요:
Determination and comparison of nitrated-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons measured in air and diesel particulate reference materials
Bamford AH, et al.
Chemosphere, 50 (5), 575-587 (2003)
Myong Gyong Lee et al.
American journal of respiratory cell and molecular biology, 38(3), 300-309 (2007-09-29)
1-Nitronaphthalene (1-NN) and ozone are cytotoxic air pollutants commonly found as components of photochemical smog. The mechanism of toxicity for 1-NN involves bioactivation by cytochrome P450s and subsequent adduction to proteins. Previous studies have shown that 1-NN toxicity in the
J Azmi et al.
Biomarkers : biochemical indicators of exposure, response, and susceptibility to chemicals, 10(6), 401-416 (2005-11-26)
Metabolic fingerprints, in the form of patterns of high-concentration endogenous metabolites, of 1-nitronaphthalene (NN)-induced lung toxicity have been elucidated in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), urine, blood plasma, and intact lung and liver tissue using NMR spectroscopy-based metabolic profiling. A single
Gregory L Baker et al.
Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology, 77(1), 135-141 (2003-11-06)
The mechanisms of toxicant-mediated lung injury and repair are influenced by the considerable spatial heterogeneity that exists within the conducting airways of the lungs. As a result of this heterogeneity, significant differences and similarities in gene expression are observed throughout
Ching Yu Lin et al.
Proteomics, 6(3), 972-982 (2006-02-03)
Naphthalene and 1-nitronaphthalene are ambient air pollutants, which undergo P450-dependent bioactivation in the lung. Reactive metabolites of naphthalene and 1-nitronaphthalene covalently bind to proteins, and the formation of covalent adducts correlates with airway epithelial cell injury in rodent models. These
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.