MABE1109
Anti-HHV-8 LNA-1 Antibody, clone LN53
clone LN53, from rat
동의어(들):
HHV-8/KSHV Orf73 LANA, HHV-8/KSHV Orf73 LNA, HHV-8/KSHV Orf73 LNA-1, HHV-8/KSHV Orf73 latency-associated nuclear antigen, HHV-8/KSHV Orf73 latent nuclear antigen, HHV-8/KSHV Orf73 latent nuclear antigen-1
로그인조직 및 계약 가격 보기
모든 사진(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC 코드:
12352203
eCl@ss:
32160702
NACRES:
NA.41
추천 제품
생물학적 소스
rat
Quality Level
항체 형태
purified immunoglobulin
항체 생산 유형
primary antibodies
클론
LN53, monoclonal
종 반응성
human, rhesus macaque
기술
ELISA: suitable
flow cytometry: suitable
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
동형
IgG2cκ
GenBank 수납 번호
NCBI 수납 번호
배송 상태
ambient
타겟 번역 후 변형
unmodified
관련 카테고리
일반 설명
Human herpesvirus-8//Kaposi′s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (HHV-8/KSHV) and macaque retroperitoneal fibromatosis herpesvirus (RFHV) were originally identified in in AIDS patients in association with Kaposi′s sarcoma (KS) and in retroperitoneal fibromatosis (RF) tumor lesions of macaques with simian AIDS, respectively. The most prominent protein expressed in cells latently infected with KSHV and RFHV is the orf73 gene product known as the latency-associated nuclear antigen (LANA or LNA). LANA is a nuclear protein that functions to ensure the maintenance of the viral genome by tethering the viral episomal DNA to host cell chromosomes. LANA also regulates the cellular transcription program in host cells through interaction with a number of cellular proteins, including transcriptional regulators and known tumor suppressors, p53 and pRB. In addtion, LANA directly influences the viral transcription program and helps maintain the latent state of the virus by inhibiting viral replication. KSHV LANA consists of a serine- and proline-rich N-terminal domain with a nuclear localization signal (NLS), a chromatin-binding motif (CBM), and domains responsible for interaction with the transcription regulators, mSin3 complex and Sp1. The central domain contains several highly repetitive acidic regions that vary in length and are responsible for the size variation of LANA proteins from different KSHV isolates that can range from 1003 to 1162 amino acids. The proline-rich C-terminal third domain contains another NLS and is responsible for LANA dimerization and binding to the terminal repeats (TR) of the viral genomic DNA. The C-terminal domain is responsible for interaction with tumor suppressors pRB and p53.
특이성
Clone LN53 recognizes repetitive glutamic acid structural motifs EQEQE and EPEPE found in the Glu-rich repeat region of human Kaposi′s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV or HHV-8) and simian retroperitoneal fibromatosis herpesvirus (RFHV) Orf73 latency-associated nuclear antigen (LANA or LNA), respectively.
Human KSHV (HHV8) and simian RFHV.
면역원
Affinity-purified GST fusions of HHV-8 LNA-1 C-terminal fragments (Kellam, P., et al. (1999). J. Virol. 73(6): 5149 5155).
애플리케이션
Anti-HHV-8 LNA-1, clone LN53, Cat. No. MABE1109, is a highly specific rat monoclonal antibody that targets human KSHV/HHV8 and simian RFHV Orf73 latency-associated nuclear antigen (LANA or LNA) and has been tested in ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Immunocytochemistry, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitati
ELISA Analysis: A representative lot detected HHV-8 LNA-1 recombinant constructs containing the repetitive region a.a. 803-929 (Kellam, P., et al. (1999). J. Virol. 73(6): 5149 5155).
Flow Cytometry Analysis: A representative lot detected HHV-8 LNA-1 immunoreactivity in BCP-1, BC-3, and HBL-6 cells, but not in Daudi or Ramos cells (Kellam, P., et al. (1999). J. Virol. 73(6): 5149 5155).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected the transiently expressed KHSV ORF73 (HHV-8 LANA or LNA-1) as well as rhesus macaque retroperitoneal fibromatosis herpesvirus ORF73 (RFHV LANA) in the nuclei of transfected COS cells by fluorescent immunocytochemistry. No reactivity was detected toward pig-tailed macaque MneRV2 or rhesus macaque RRV LANA proteins (Burnside, K.L., et al. (2006). Virology. 354(1):103-115).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected HHV-8 LNA-1-positive nuclear bodies in primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) cell line BCP-1 by fluorescent immunocytochemistry, but not in Daudi or Ramos cells (Kellam, P., et al. (1999). J. Virol. 73(6): 5149 5155).
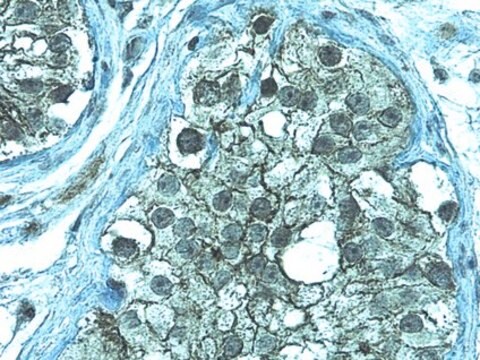
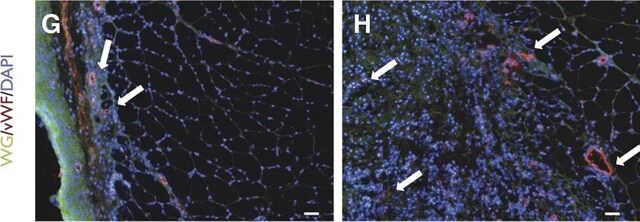
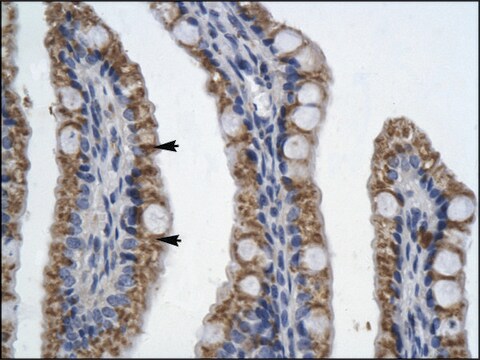
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected RFHVMn LANA immunoreactivity in the nuclei of retroperitoneal fibromatosis (RF) tumor cells by immunohistochemistry staining of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded RF biopsies from an SIV-infected pig-tailed macaque. No immunoreactivity was detected using normal macaque jejunum tissue sections (Burnside, K.L., et al. (2006). Virology. 354(1):103-115).
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: Representative lots immunostained cells latently infected by HHV-8 by immunohistochemistry staining of paraffin-embedded patch, plaque, and nodular Kaposi s sarcoma (KS), multicentric Castleman s disease (MCD), and primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) tissue sections (Codish, S., et al. (2000). Am. J. Hematol. 65(4):310-314; Dupin, N., et al. (2000). Blood. 95(4):1406-1412; Dupin, N., et al. (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96(8):4546-4551).
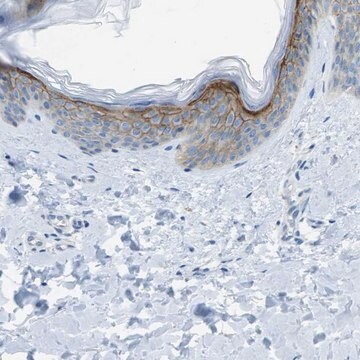
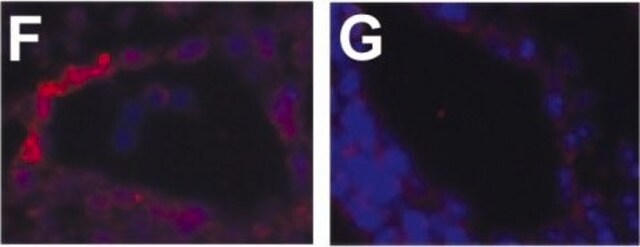
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected nuclear HHV-8 LNA-1 immunoreactivity in cells within the nodular Kaposi s sarcoma (KS) lesion, but not in the surrounding dermis by immunohistochemistry staining of paraffin-embedded classical KS tumor sections (Kellam, P., et al. (1999). J. Virol. 73(6): 5149 5155).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot immunoprecipitated 220/230 kDa HHV-8 LNA-1 from primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) cell line BC-3, but not from Ramos cells (Kellam, P., et al. (1999). J. Virol. 73(6): 5149 5155).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected the transiently expressed KHSV ORF73 (HHV-8 LANA or LNA-1) as well as rhesus macaque retroperitoneal fibromatosis herpesvirus ORF73 (RFHV LANA) in lysate from transfected COS cells. No reactivity was detected toward pig-tailed macaque MneRV2 or rhesus macaque RRV LANA proteins (Burnside, K.L., et al. (2006). Virology. 354(1):103-115).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected the 220/230 kDa HHV-8 LNA-1 doublet in lysate from primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) cell line BC-3, but not from Ramos cells (Kellam, P., et al. (1999). J. Virol. 73(6): 5149 5155).
Flow Cytometry Analysis: A representative lot detected HHV-8 LNA-1 immunoreactivity in BCP-1, BC-3, and HBL-6 cells, but not in Daudi or Ramos cells (Kellam, P., et al. (1999). J. Virol. 73(6): 5149 5155).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected the transiently expressed KHSV ORF73 (HHV-8 LANA or LNA-1) as well as rhesus macaque retroperitoneal fibromatosis herpesvirus ORF73 (RFHV LANA) in the nuclei of transfected COS cells by fluorescent immunocytochemistry. No reactivity was detected toward pig-tailed macaque MneRV2 or rhesus macaque RRV LANA proteins (Burnside, K.L., et al. (2006). Virology. 354(1):103-115).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected HHV-8 LNA-1-positive nuclear bodies in primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) cell line BCP-1 by fluorescent immunocytochemistry, but not in Daudi or Ramos cells (Kellam, P., et al. (1999). J. Virol. 73(6): 5149 5155).
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected RFHVMn LANA immunoreactivity in the nuclei of retroperitoneal fibromatosis (RF) tumor cells by immunohistochemistry staining of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded RF biopsies from an SIV-infected pig-tailed macaque. No immunoreactivity was detected using normal macaque jejunum tissue sections (Burnside, K.L., et al. (2006). Virology. 354(1):103-115).
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: Representative lots immunostained cells latently infected by HHV-8 by immunohistochemistry staining of paraffin-embedded patch, plaque, and nodular Kaposi s sarcoma (KS), multicentric Castleman s disease (MCD), and primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) tissue sections (Codish, S., et al. (2000). Am. J. Hematol. 65(4):310-314; Dupin, N., et al. (2000). Blood. 95(4):1406-1412; Dupin, N., et al. (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96(8):4546-4551).
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected nuclear HHV-8 LNA-1 immunoreactivity in cells within the nodular Kaposi s sarcoma (KS) lesion, but not in the surrounding dermis by immunohistochemistry staining of paraffin-embedded classical KS tumor sections (Kellam, P., et al. (1999). J. Virol. 73(6): 5149 5155).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot immunoprecipitated 220/230 kDa HHV-8 LNA-1 from primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) cell line BC-3, but not from Ramos cells (Kellam, P., et al. (1999). J. Virol. 73(6): 5149 5155).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected the transiently expressed KHSV ORF73 (HHV-8 LANA or LNA-1) as well as rhesus macaque retroperitoneal fibromatosis herpesvirus ORF73 (RFHV LANA) in lysate from transfected COS cells. No reactivity was detected toward pig-tailed macaque MneRV2 or rhesus macaque RRV LANA proteins (Burnside, K.L., et al. (2006). Virology. 354(1):103-115).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected the 220/230 kDa HHV-8 LNA-1 doublet in lysate from primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) cell line BC-3, but not from Ramos cells (Kellam, P., et al. (1999). J. Virol. 73(6): 5149 5155).
품질
Evaluated by Immunocytochemistry in BCBL-1 cells.
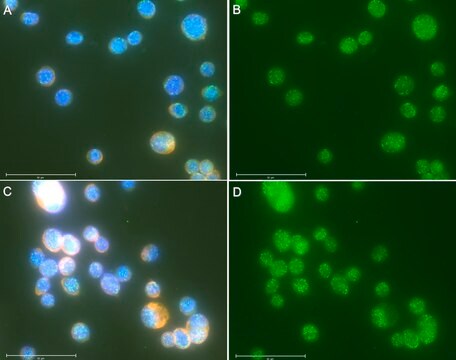
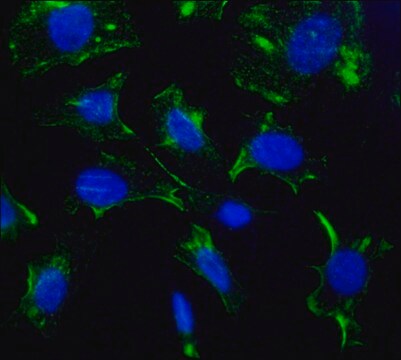
Immunocytochemistry Analysis (ICC): 1 µg/mL of this antibody immunostained HHV-8 LNA-1-positive nuclear bodies in Kaposi′s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus 8- (KSHV/HHV8-) infected BCBL-1 lymphoma cells.
Immunocytochemistry Analysis (ICC): 1 µg/mL of this antibody immunostained HHV-8 LNA-1-positive nuclear bodies in Kaposi′s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus 8- (KSHV/HHV8-) infected BCBL-1 lymphoma cells.
표적 설명
116/135 kDa (KSHV LNA) and 118 kDa (RFHV LNA) prediced, ~220/230 kDa doublet (KSHV) and ~240 kDa doublet (RFHV) reported (Burnside, K.L., et al. (2006). Virology. 354(1):103-115; Kellam, P., et al. (1999). J. Virol. 73(6): 5149 5155). The larger-than-predicted apparent molecular weight is most likely caused by the internal acidic repeat region sequence (Rainbow, L., et al. (1997). J. Virol. 71(8):5915-5921).
물리적 형태
Format: Purified
Purified rat monoclonal IgG2c in buffer containing 0.1 M Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4) 150 mM NaCl with 0.05% sodium azide
기타 정보
Concentration: Please refer to lot specific datasheet.
법적 정보
GenBank is a registered trademark of United States Department of Health and Human Services
적합한 제품을 찾을 수 없으신가요?
당사의 제품 선택기 도구.을(를) 시도해 보세요.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
시험 성적서(COA)
제품의 로트/배치 번호를 입력하여 시험 성적서(COA)을 검색하십시오. 로트 및 배치 번호는 제품 라벨에 있는 ‘로트’ 또는 ‘배치’라는 용어 뒤에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
Min Tan et al.
Nucleic acids research, 49(22), 12895-12911 (2021-12-02)
Mixed lineage leukemia 1 (MLL1) is a histone methyltransferase. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is a leading cause of malignancy in AIDS. KSHV latently infects tumor cells and its genome is decorated with epigenetic marks. Here, we show that KSHV latency-associated
Ashish Kumar et al.
Cell reports, 39(6), 110788-110788 (2022-05-12)
Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) establishes a latent infection in the cell nucleus, but where KSHV episomal genomes are tethered and the mechanisms underlying KSHV lytic reactivation are unclear. Here, we study the nuclear microenvironment of KSHV episomes and show that
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.