추천 제품
생물학적 소스
mouse
Quality Level
항체 형태
purified immunoglobulin
항체 생산 유형
primary antibodies
클론
NE14, monoclonal
종 반응성
rat, pig, human
제조업체/상표
Chemicon®
기술
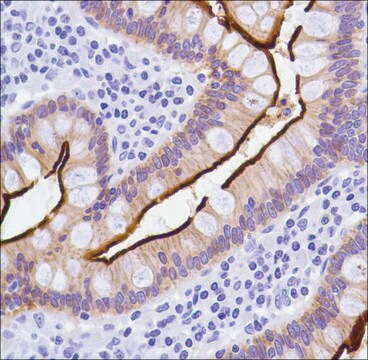
immunohistochemistry: suitable
동형
IgG1
NCBI 수납 번호
UniProt 수납 번호
배송 상태
wet ice
타겟 번역 후 변형
unmodified
유전자 정보
human ... NEFH(4744)
pig ... Nefh(100156492)
rat ... Nefh(24587)
일반 설명
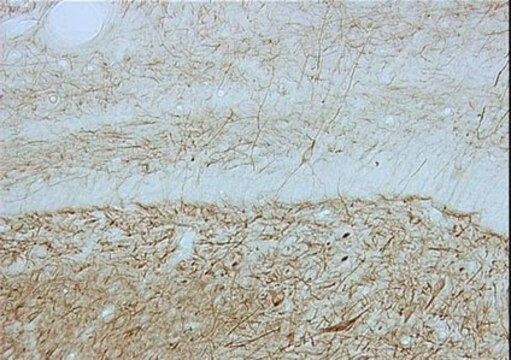
Neurofilaments are a type of intermediate filament that serve as major elements of the cytoskeleton supporting the axon cytoplasm. They are the most abundant fibrillar components of the axon, being on average 3-10 times more frequent than axonal microtubules. Neurofilaments (10nm in dia.) are built from three intertwined protofibrils which are themselves composed of two tetrameric protofilament complexs of monomeric proteins. The neurofilament triplet proteins (68/70, 160, and 200 kDa) occur in both the central and peripheral nervous system and are usually neuron specific. The 68/70 kDa NF-L protein can self-assemble into a filamentous structure, however the 160 kDa NF-M and 200 kDa NF-H proteins require the presence of the 68/70 kDa NF-L protein to co-assemble. Neuromas, ganglioneuromas, gangliogliomas, ganglioneuroblastomas and neuroblastomas stain positively for neurofilaments. Although typically restricted to neurons, neurofilaments have been detected in paragangliomas and adrenal and extra-adrenal pheochromocytomas. Carcinoids, neuroendocrine carcinomas of the skin, and oat cell carcinomas of the lung also express neurofilaments. For more neurofilament information see Nervous System Cell Type Specific Marker chart online under the CHEMICON Technical Support section.
특이성
The antibody reacts with neurofilament 200 kD.
면역원
Purified neurofilament polypeptides (Debus et al., 1983).
애플리케이션
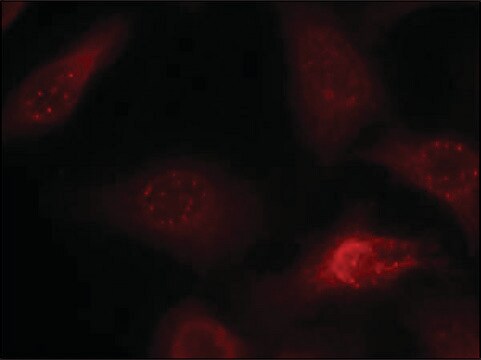
Detect Neurofilament 200 kDa using this Anti-Neurofilament 200 kDa Antibody, clone NE14 validated for use in IH.
Immunohistochemistry: 5-10 μg/mL (See below protocol.)
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Immunohistochemistry Protocol for Anti-Neurofilament 200 kD
Ideal specimens are obtained from frozen sections from shock-frozen tissue samples. The frozen sections are dried in the air and then fixed with acetone at -15 to -25°C for 10 min. Excess acetone is allowed to evaporate at 15-25°C. Material fixed in alcohol and embedded in paraffin can also be used, see (Altmannsberger et al., 1982). The antibody appears to react with tissue fixed in formaldehyde for a short time (10 min) (Debus et al., 1983). Other fixation conditions must be first tested by the investigator.
It is advantageous to block unspecific binding sites by overlaying the sections with fetal calf serum for 20-30 min at 15-25°C. Excess of fetal calf serum is removed by decanting before application of the antibody solution. Cytocentrifuge preparations of single cells or cell smears are also fixed in acetone. These preparations should, however, not be dried in the air. Instead, the excess acetone is removed by briefly washing in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS).
Further treatment is then as follows:
Overlay the preparation with 10-20 μL antibody solution and incubate in a humid chamber at 37°C for 1 h.
Dip the slide briefly in PBS and then wash 3 times in PBS for 3 min (use fresh PBS each time)
Wipe the margins of the preparation dry and overlay the preparation with 10-20 μL of an anti-mouse Ig-FITC or anti-mouse Ig-POD antibody and allow to incubate for 1 h at 37°C in a humid chamber.
Wash the slide as described above.
The preparation must not be allowed to dry out during any of the steps.
If using an indirect immunofluorescence technique, the preparation should be overlaid with a suitable embedding medium (e.g. Moviol, Hoechst) and examined under the fluorescence microscope. If a POD-conjugate has been used as the secondary antibody, the preparation should be overlaid with a substrate solution (see below) and incubated at 15-25°C until a clearly visible red-brown color develops. A negative control (e.g. only the secondary antibody) should remain unchanged in color during this incubation period. Subsequently, the substrate is washed off with PBS and the preparation is stained, if desired, with hemalum stain for about 1 min. The hemalum solution is washed off with PBS, the preparation is embedded and examined.
Substrate solutions:
Aminoethyl-carbazole:
Dissolve 2 mg 3-amino-9-ethylcarbazole with 1.2 mL dimethylsulfoxide and add 28.8 mL 0.05 M Tris-HCl, pH 7.3, and 20 μL 3% H 2 O 2 (w/v). Prepare solution freshly each day.
Diaminobenzidine:
Dissolve 25 mg 3,3′-diaminobenzidine with 50 mL 0.05 M Tris-HCl, pH 7.3, and add 40 μL 3% H2O2 (w/v). Prepare solution freshly each day.
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Immunohistochemistry Protocol for Anti-Neurofilament 200 kD
Ideal specimens are obtained from frozen sections from shock-frozen tissue samples. The frozen sections are dried in the air and then fixed with acetone at -15 to -25°C for 10 min. Excess acetone is allowed to evaporate at 15-25°C. Material fixed in alcohol and embedded in paraffin can also be used, see (Altmannsberger et al., 1982). The antibody appears to react with tissue fixed in formaldehyde for a short time (10 min) (Debus et al., 1983). Other fixation conditions must be first tested by the investigator.
It is advantageous to block unspecific binding sites by overlaying the sections with fetal calf serum for 20-30 min at 15-25°C. Excess of fetal calf serum is removed by decanting before application of the antibody solution. Cytocentrifuge preparations of single cells or cell smears are also fixed in acetone. These preparations should, however, not be dried in the air. Instead, the excess acetone is removed by briefly washing in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS).
Further treatment is then as follows:
Overlay the preparation with 10-20 μL antibody solution and incubate in a humid chamber at 37°C for 1 h.
Dip the slide briefly in PBS and then wash 3 times in PBS for 3 min (use fresh PBS each time)
Wipe the margins of the preparation dry and overlay the preparation with 10-20 μL of an anti-mouse Ig-FITC or anti-mouse Ig-POD antibody and allow to incubate for 1 h at 37°C in a humid chamber.
Wash the slide as described above.
The preparation must not be allowed to dry out during any of the steps.
If using an indirect immunofluorescence technique, the preparation should be overlaid with a suitable embedding medium (e.g. Moviol, Hoechst) and examined under the fluorescence microscope. If a POD-conjugate has been used as the secondary antibody, the preparation should be overlaid with a substrate solution (see below) and incubated at 15-25°C until a clearly visible red-brown color develops. A negative control (e.g. only the secondary antibody) should remain unchanged in color during this incubation period. Subsequently, the substrate is washed off with PBS and the preparation is stained, if desired, with hemalum stain for about 1 min. The hemalum solution is washed off with PBS, the preparation is embedded and examined.
Substrate solutions:
Aminoethyl-carbazole:
Dissolve 2 mg 3-amino-9-ethylcarbazole with 1.2 mL dimethylsulfoxide and add 28.8 mL 0.05 M Tris-HCl, pH 7.3, and 20 μL 3% H 2 O 2 (w/v). Prepare solution freshly each day.
Diaminobenzidine:
Dissolve 25 mg 3,3′-diaminobenzidine with 50 mL 0.05 M Tris-HCl, pH 7.3, and add 40 μL 3% H2O2 (w/v). Prepare solution freshly each day.
Research Category
Neuroscience
Neuroscience
Research Sub Category
Neurofilament & Neuron Metabolism
Neuronal & Glial Markers
Neurofilament & Neuron Metabolism
Neuronal & Glial Markers
물리적 형태
Format: Purified
Purified immunoglobulin. Liquid. Buffer = 0.02M Phosphate buffer, 0.25M NaCl containing 0.1% sodium azide.
저장 및 안정성
Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C in undiluted aliquots for up to 6 months.DO NOT FREEZE
기타 정보
Concentration: Please refer to the Certificate of Analysis for the lot-specific concentration.
법적 정보
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
면책조항
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
적합한 제품을 찾을 수 없으신가요?
당사의 제품 선택기 도구.을(를) 시도해 보세요.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
시험 성적서(COA)
제품의 로트/배치 번호를 입력하여 시험 성적서(COA)을 검색하십시오. 로트 및 배치 번호는 제품 라벨에 있는 ‘로트’ 또는 ‘배치’라는 용어 뒤에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
Neurochemical characterization of insulin receptor-expressing primary sensory neurons in wild-type and vanilloid type 1 transient receptor potential receptor knockout mice.
Djalil Baiou,Peter Santha,Antonio Avelino,Ana Charrua,Timea Bacskai,Klara Matesz et al.
The Journal of Comparative Neurology null
Immunohistochemical localization of histamine receptor subtypes in human inferior turbinates.
Muneo Nakaya, Naonobu Takeuchi, Kenji Kondo
The Annals of Otology, Rhinology, and Laryngology null
Asiyeh Golabchi et al.
Biosensors & bioelectronics, 155, 112096-112096 (2020-02-25)
Intracortical microelectrodes are being developed to both record and stimulate neurons to understand brain circuitry or restore lost functions. However, the success of these probes is hampered partly due to the inflammatory host tissue responses to implants. To minimize the
Takashi D Y Kozai et al.
Biomaterials, 35(36), 9620-9634 (2014-09-02)
Chronic implantation of microelectrodes into the cortex has been shown to lead to inflammatory gliosis and neuronal loss in the microenvironment immediately surrounding the probe, a hypothesized cause of neural recording failure. Caspase-1 (aka Interleukin 1β converting enzyme) is known
Asiyeh Golabchi et al.
Biomaterials, 225, 119519-119519 (2019-10-11)
The inflammatory brain tissue response to implanted neural electrode devices has hindered the longevity of these implants. Zwitterionic polymers have a potent anti-fouling effect that decreases the foreign body response to subcutaneous implants. In this study, we developed a nanoscale
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.