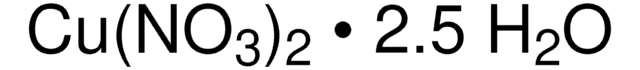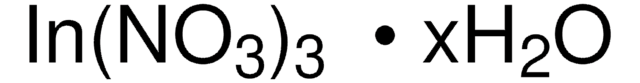940143
Copper(II) nitrate trihydrate
≥99.9% trace metals basis
동의어(들):
Copper dinitrate trihydrate, Copper(2+) nitrate trihydrate, Cupric nitrate trihydrate
로그인조직 및 계약 가격 보기
모든 사진(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
Cu(NO3)2 · 3H2O
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
241.60
MDL number:
UNSPSC 코드:
12141711
solubility:
water: soluble
추천 제품
Grade
for analytical purposes
Quality Level
분석
(iodometric, redox titration)
≥99.9% trace metals basis
양식
(Crystal or Powder)
solubility
water: soluble
음이온 미량물
chloride (Cl-): ≤20 ppm
sulfate (SO42-): ≤50 ppm
양이온 미량물
Al: ≤10 ppm
Ca: ≤10 ppm
Cd: ≤10 ppm
Cr: ≤10 ppm
Fe: ≤10 ppm
K: ≤10 ppm
Mg: ≤10 ppm
Mn: ≤10 ppm
Na: ≤30 ppm
Ni: ≤10 ppm
Pb: ≤10 ppm
Si: ≤10 ppm
Zn: ≤10 ppm
SMILES string
[Cu+2].[N+](=O)([O-])[O-].[N+](=O)([O-])[O-].O.O.O
InChI key
SXTLQDJHRPXDSB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
일반 설명
Copper(II) nitrate trihydrate is a crystalline compound with high solubility in water. It serves as an excellent precursor for the synthesis of high-purity compounds, nanomaterials, and catalysts.
애플리케이션
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have found applications in various fields such as gas storage, separations, sensors, catalysis, fuel cells, solar cells, nanotechnology devices, and drug delivery. Through a modular assembly strategy, a highly crystalline thin film of Cu-TCPP MOF was synthesized using Copper(II) nitrate trihydrate and the linker TCPP. This specific MOF holds significant promise due to its well-defined structure and potential for diverse applications. -Copper oxide nanoparticles of varying sizes were synthesized through a hydrothermal method using different concentrations of Copper(II) nitrate trihydrate. The pH of the solution was adjusted by adding NaOH or HNO3. This versatile approach allowed for the controlled synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles with different sizes. - Mesoporous CuCo2O4 nanowires were synthesized as electrode materials for supercapacitors using Copper(II) nitrate trihydrate and Cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate using hydrothermal method. The synthesis involved nanocasting from a silica SBA-15 template. These electrode materials exhibited a capacitance of 1210 F g–1 at a current density of 2 A g–1, which significantly increased upon cycling to exceed 3000 F g–1. - A hybrid electrode comprising CuO and Cu2O micronanoparticles within a graphitized porous carbon matrix was synthesized using Copper(II) nitrate trihydrate via a one-step thermal transformation process. This hybrid electrode exhibited remarkable performance when employed as a negative electrode in lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries, achieving capacities of 887.3 mAh g–1 at 60 mA g–1 and 302.9 mAh g–1 at 50 mA g–1 after 200 cycles, respectively. In addition,Copper(II) nitrate trihydrate serves as a suitable precursor for synthesizing copper catalysts for various applications. -Copper ferrite catalysts were synthesized using a co-precipitation method with the salt precursors Copper(II) nitrate trihydrate and Fe(NO3)3·9H2O. These catalysts exhibited heightened activity in the water-gas shift reaction. The improved catalytic performance can be attributed to factors such as enhanced Cu dispersion, a higher quantity of surface copper atoms, the presence of weak basic sites, and a strong interaction between copper and iron oxides, all resulting from the formation of copper ferrite.
신호어
Danger
유해 및 위험 성명서
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Eye Dam. 1 - Ox. Sol. 2 - Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class Code
5.1B - Oxidizing hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
가장 최신 버전 중 하나를 선택하세요:
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.