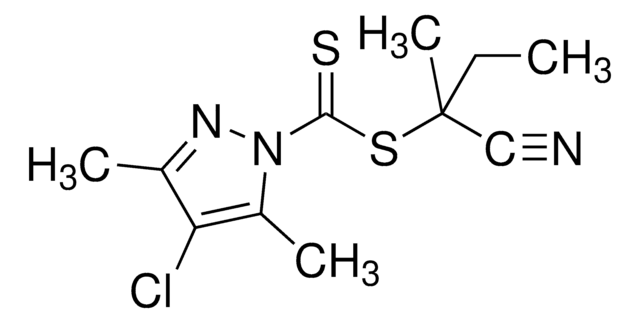
추천 제품
Quality Level
분석
97% (HPLC)
형태
liquid
refractive index
n20/D 1.535
density
0.991 g/mL at 25 °C
저장 온도
2-8°C
SMILES string
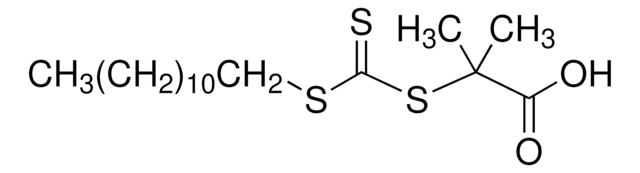
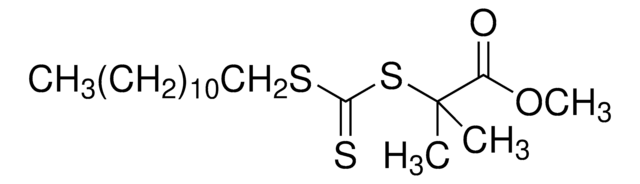
CCCCCCCCCCCCSC(=S)SC(C)(C)C#N
InChI
1S/C17H31NS3/c1-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-20-16(19)21-17(2,3)15-18/h4-14H2,1-3H3
InChI key
QSVOWVXHKOQYIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
일반 설명
애플리케이션
이미 열람한 고객
문서
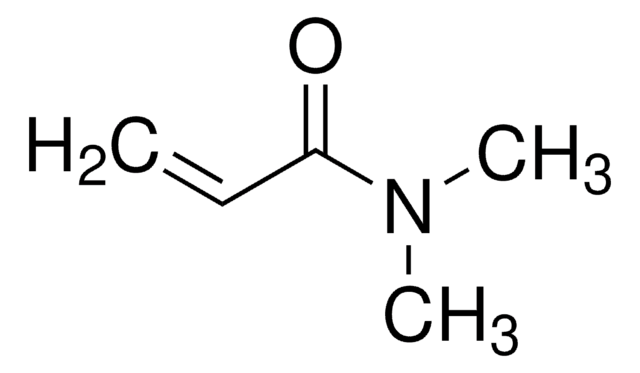
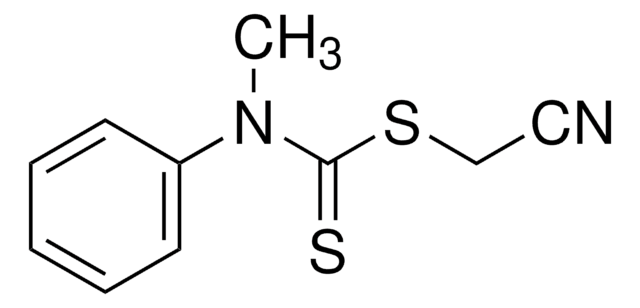
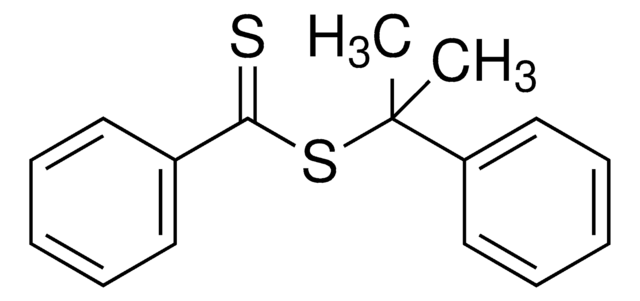
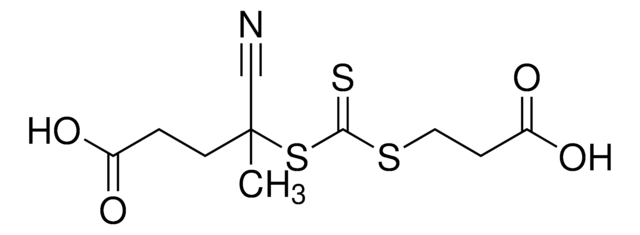
A series of polymerization were carried out using RAFT agents and monomers yielding well-defined polymers with narrow molecular weight distributions. The process allows radical-initiated growing polymer chains to degeneratively transfer reactivity from one to another through the use of key functional groups (dithioesters, trithiocarbonates, xanthates and dithiocarbamates). RAFT agents help to minimize out-of-control growth and prevent unwanted termination events from occurring, effectively controlling polymer properties like molecular weight and polydispersity. RAFT agents are commercially available. RAFT does not use any cytotoxic heavy metal components (unlike ATRP).
RAFT (Reversible Addition Fragmentation chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
Over the past two decades, the rapid advance of controlled living polymerization (CLP) techniques.
The modification of biomacromolecules, such as peptides and proteins, through the attachment of synthetic polymers has led to a new family of highly advanced biomaterials with enhanced properties.
프로토콜
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.
![4-Cyano-4-[(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonyl)sulfanyl]pentanoic acid 97% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/204/925/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af/640/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af.png)
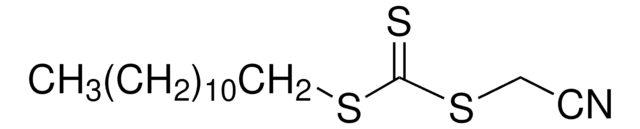

![2-[[(2-Carboxyethyl)sulfanylthiocarbonyl]-sulfanyl]propanoic acid](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/427/606/b02310e2-102e-4324-b09d-e4c0de4fab2c/640/b02310e2-102e-4324-b09d-e4c0de4fab2c.png)